Page 4 - 3. SKI_ MI_ KELAS_III_KSKK_2020_Kamimadrasah
P. 4
inequalities and responsible consumption and production respectively), no performance index was assigned due to some Kualitatif
data limitations ( Sachs et al., 2018 ). bukti dari
2.2.1 Islamic perspective on sustainable development goals. Dariah et al. ( 2016) argued that Islam with the Indonesia
concept of maqasid al-Shar ī ’ ah as promoted by Muslim scholars, including by al-Ghazal ī ( d.505 AH/1111 CE),
have been endorsing more comprehensive view on human development than SDGs. However, with its general
goal, in a particular point, one may opine that SDGs and maqasid al-Shar ī ’ ah are in line as fundamentally
explained in 357
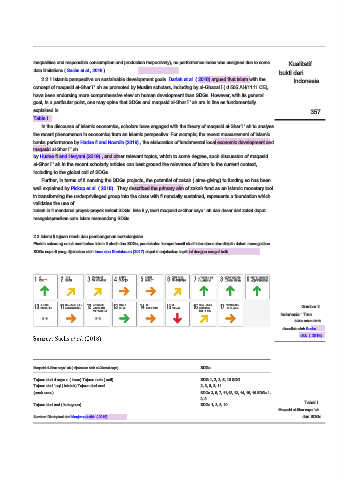
Table I .
In the discourse of Islamic economics, scholars have engaged with the theory of maqasid al-Shar ī ’ ah to analyse
the recent phenomenon in economics from an Islamic perspective. For example; the recent measurement of Islamic
banks performance by Hudae fi and Noordin (2019) , the elaboration of fundamental local economic development and
maqasid al-Shar ī ’ ah
by Hudae fi and Heryani (2019) , and other relevant topics, which to some degree, such discussion of maqasid
al-Shar ī ’ ah in the recent scholarly articles can best ground the relevance of Islam to the current context,
including to the global call of SDGs.
Further, in terms of fi nancing the SDGs projects, the potential of zakah ( alms-giving) to funding so has been
well explained by Pickup et al. ( 2018) . They described the primary aim of zakah fund as an Islamic monetary tool
in transforming the underprivileged group into the class with fi nancially sustained, represents a foundation which
validates the use of
zakah in fi mendanai proyek-proyek terkait SDGs. Brie fl y, teori maqasid al-Shar saya ' ah dan dasar dari zakat dapat
mengekspresikan cara Islam memandang SDGs.
2.3 Islami fi tujuan ntech dan pembangunan berkelanjutan
Pindah sekarang untuk membahas Islam fi ntech dan SDGs, pendekatan komprehensif studi intra-dan-antar-disiplin dalam menegakkan
SDGs seperti yang dijelaskan oleh Imaz dan Sheinbaum (2017) dapat menjelaskan topik ini dengan sangat baik.
Gambar 2.
Indonesia ' Tren
SDGs tahun 2018
dianalisis oleh Sachs
dkk. ( 2018)
Maqasid al-Shar saya ' ah ( dijelaskan oleh al-Ghazal saya) SDGs
Tujuan dari d saya n ( iman) Tujuan nafs ( self) SDG 1, 2, 3, 6, 10 SDG
Tujuan dari ' aql ( intelek) Tujuan dari nasl 2, 3, 6, 8, 11
(anak cucu) SDGs 3, 5, 7, 11,12, 13, 14, 15, 16 SDGs 1,
2, 9
Tujuan dari mal ( kekayaan) SDGs 1, 3, 8, 10 Tabel I.
Maqasid al-Shar saya ' ah
Sumber: Diadaptasi dari Menjemput dkk. ( 2018) dan SDGs