Page 86 - Grammar for Great Writing B
P. 86
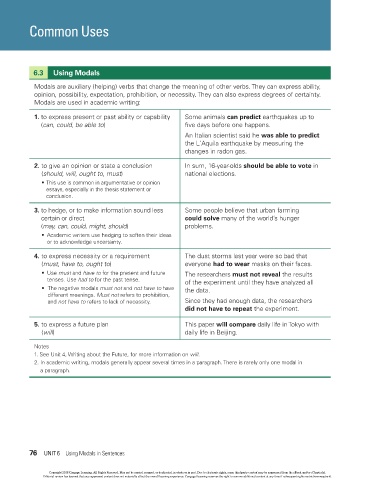
Common Uses
6.3 Using Modals
Modals are auxiliary (helping) verbs that change the meaning of other verbs. They can express ability,
opinion, possibility, expectation, prohibition, or necessity. They can also express degrees of certainty.
Modals are used in academic writing:
1. to express present or past ability or capability Some animals can predict earthquakes up to
(can, could, be able to) five days before one happens.
An Italian scientist said he was able to predict
the L’Aquila earthquake by measuring the
changes in radon gas.
2. to give an opinion or state a conclusion In sum, 16-year-olds should be able to vote in
(should, will, ought to, must) national elections.
• This use is common in argumentative or opinion
essays, especially in the thesis statement or
conclusion.
3. to hedge, or to make information sound less Some people believe that urban farming
certain or direct could solve many of the world’s hunger
(may, can, could, might, should) problems.
• Academic writers use hedging to soften their ideas
or to acknowledge uncertainty.
4. to express necessity or a requirement The dust storms last year were so bad that
(must, have to, ought to) everyone had to wear masks on their faces.
• Use must and have to for the present and future The researchers must not reveal the results
tenses. Use had to for the past tense. of the experiment until they have analyzed all
• The negative modals must not and not have to have the data.
different meanings. Must not refers to prohibition,
and not have to refers to lack of necessity. Since they had enough data, the researchers
did not have to repeat the experiment.
5. to express a future plan This paper will compare daily life in Tokyo with
(will) daily life in Beijing.
Notes
1. See Unit 4, Writing about the Future, for more information on will.
2. In academic writing, modals generally appear several times in a paragraph. There is rarely only one modal in
a paragraph.
76 Unit 6 Using Modals in Sentences
Copyright 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Copyright 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s).
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.
Editorial review has deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.
Copyright 2018 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. WCN 02-200-203
072-085_18606_GGW_SB_B_U6.indd 76 12/14/16 3:02 PM