Page 21 - Апрель
P. 21
METALWORKING EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS
cutters cannot guarantee the stability of the surface layer of the part, since the radial wear
can be formally converted into wear on the flank face, but the uncertainty of the force effect
on the surface of the part will remain large due to the random nature of fractures within wear
chamfers. The corner radius is only statistically related to the flank wear chamfer. In addition,
modeling the destruction of the cutting edge in the form of a section of a cylindrical surface is
often only a distant approximation to the real type of wear, which may depend not only on the
processing modes, but also on the tool and processed materials [9, 10, 14].
When examining worn cutters under a microscope, it is difficult to find a similarity between
the cylindrical surface and the actual shape of the cutting edge. Within the wear area, there
are numerous small chips and notches, the shape of which is of a random nature. The purpose
of this research is to create an integrated system for ensuring the quality of the surface layer
during blade processing by controlling indirect parameters. It is known that the destruction of
the cutting edge, causing severe deformations of the machined surface, leads to an increase in
the consumed energy, corresponding to an increase in cutting forces and the amount of heat
generated. The control of the cutting forces can be carried out by changing the active power
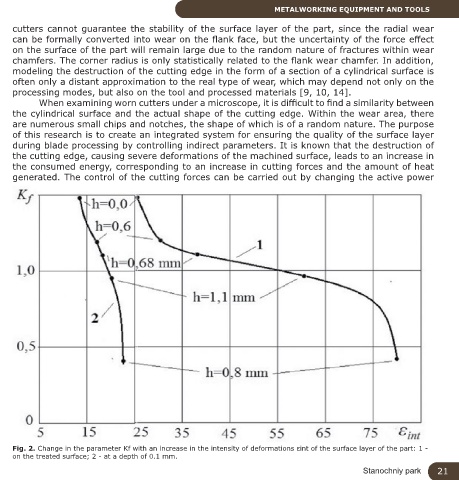
Fig. 2. Change in the parameter Кf with an increase in the intensity of deformations εint of the surface layer of the part: 1 -
on the treated surface; 2 - at a depth of 0.1 mm.
Stanochniy park 21