Page 162 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 162
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
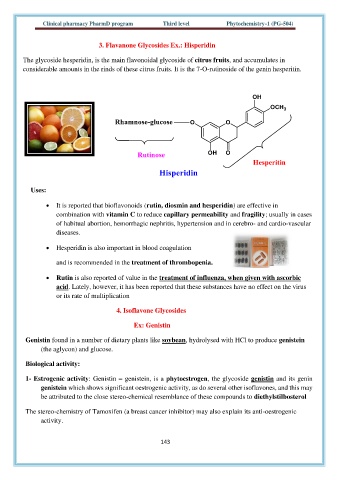
3. Flavanone Glycosides Ex.: Hisperidin
The glycoside hesperidin, is the main flavonoidal glycoside of citrus fruits, and accumulates in
considerable amounts in the rinds of these citrus fruits. It is the 7-O-rutinoside of the genin hesperitin.
Uses:
• It is reported that bioflavonoids (rutin, diosmin and hesperidin) are effective in
combination with vitamin C to reduce capillary permeability and fragility; usually in cases
of habitual abortion, hemorrhagic nephritis, hypertension and in cerebro- and cardio-vascular
diseases.
• Hesperidin is also important in blood coagulation
and is recommended in the treatment of thrombopenia.
• Rutin is also reported of value in the treatment of influenza, when given with ascorbic
acid. Lately, however, it has been reported that these substances have no effect on the virus
or its rate of multiplication
4. Isoflavone Glycosides
Ex: Genistin
Genistin found in a number of dietary plants like soybean, hydrolysed with HCl to produce genistein
(the aglycon) and glucose.
Biological activity:
1- Estrogenic activity: Genistin = genistein, is a phytoestrogen, the glycoside genistin and its genin
genistein which shows significant oestrogenic activity, as do several other isoflavones, and this may
be attributed to the close stereo-chemical resemblance of these compounds to diethylstilbosterol
The stereo-chemistry of Tamoxifen (a breast cancer inhibitor) may also explain its anti-oestrogenic
activity.
143