Page 52 - PG 504-theoretical notes-phyto-1-2024-2025..
P. 52
Clinical pharmacy PharmD program Third level Phytochemistry-1 (PG-504)
C) Action of Oxidizing Cations:
Mono-, di- and some polysaccharides which contain free anomeric carbon
(i.e., a sugar group), undergo oxidation in the presence of oxidizing cations such
++
as Cu in alkaline solution (e. g., Fehling’s reagent, Benedict’s reagent).
D) Action of Acids on Monosaccharide:
• The effect of acids on monosaccharide depends on:
a) Concentration b) Temperature
i. Dilute non-oxidizing acid at room temperature:
In this case the monosaccharide is stable.
ii. Hot concentrated acids:
▪ Hot concentrated hydrochloric acid eliminates water from the sugar
molecule with the formation of non-carbohydrate (i.e., furan derivatives):
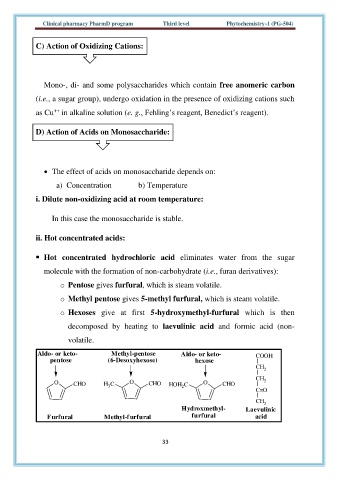
o Pentose gives furfural, which is steam volatile.
o Methyl pentose gives 5-methyl furfural, which is steam volatile.
o Hexoses give at first 5-hydroxymethyl-furfural which is then
decomposed by heating to laevulinic acid and formic acid (non-
volatile.
Aldo- or keto- Methyl-pentose Aldo- or keto- COOH
pentose (6-Desoxyhexose) hexose
CH 2
CH
O CHO H C O CHO HOH C O CHO 2
3
2
C=O
CH 3
Hydroxmethyl- Laevulinic
Furfural Methyl-furfural furfural acid
33