Page 130 - DUOKOPT BIBLIOBOOK
P. 130
DUOKOPT - bibliography book - CONFIDENTIAL - document for exclusive use by personnel of Laboratoires Théa – DO NOT DISTRIBUTE
®
Results of 1-year fixed combination glaucoma treatment
treatment in both groups. We did not observe significant
fluctuations in IOP between the study visits (p>0.05). We
chose to compare the 2 combination treatments because
we expected both to have similar effects on IOP and dif-
ferent effects on OP and retrobulbar circulation. Different
results were reported regarding the effect of dorzolamide
(component of DTFC) on ocular blood flow; some studies
reported increase in ocular blood flow (16-22) and others
showed no positive effect (23-25).
We found some differences in baseline CDI and BP param-
eters that could be explained by differences in age (DTFC
group 56.93 [9.54] and LTFC group 59.33 [7.696] years [t
test; p=0.455]) and sex: the study population consisted
of 5 men (16.7%) and 25 women (83.3%). After random
assignment, 1 man entered the DTFC group (6.6% of the
DTFC group) and 4 the LTFC group (26.6% of the LTFC
group). The LTFC treatment group showed statistically sig-
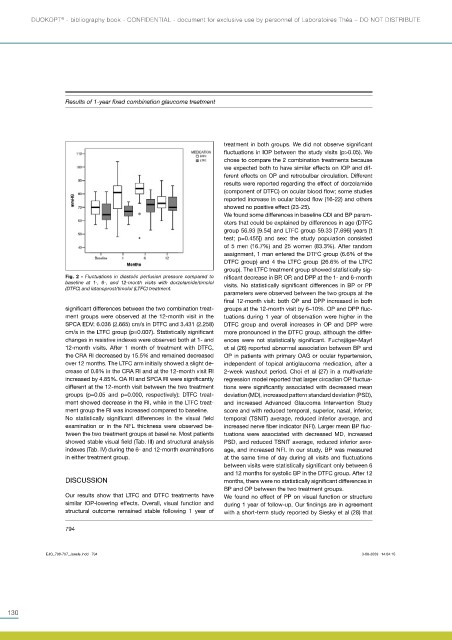
Fig. 2 - Fluctuations in diastolic perfusion pressure compared to nificant decrease in BP, OP, and DPP at the 1- and 6-month
baseline at 1-, 6-, and 12-month visits with dorzolamide/timolol visits. No statistically significant differences in BP or PP
(DTFC) and latanoprost/timolol (LTFC) treatment.
parameters were observed between the two groups at the
final 12-month visit: both OP and DPP increased in both
significant differences between the two combination treat- groups at the 12-month visit by 6–10%. OP and DPP fluc-
ment groups were observed at the 12-month visit in the tuations during 1 year of observation were higher in the
SPCA EDV: 6.036 (2.665) cm/s in DTFC and 3.431 (2.258) DTFC group and overall increases in OP and DPP were
cm/s in the LTFC group (p=0.007). Statistically significant more pronounced in the DTFC group, although the differ-
changes in resistive indexes were observed both at 1- and ences were not statistically significant. Fuchsjäger-Mayrl
12-month visits. After 1 month of treatment with DTFC, et al (26) reported abnormal association between BP and
the CRA RI decreased by 15.5% and remained decreased OP in patients with primary OAG or ocular hypertension,
over 12 months. The LTFC arm initially showed a slight de- independent of topical antiglaucoma medication, after a
crease of 0.8% in the CRA RI and at the 12-month visit RI 2-week washout period. Choi et al (27) in a multivariate
increased by 4.85%. OA RI and SPCA RI were significantly regression model reported that larger circadian OP fluctua-
different at the 12-month visit between the two treatment tions were significantly associated with decreased mean
groups (p=0.05 and p=0.000, respectively): DTFC treat- deviation (MD), increased pattern standard deviation (PSD),
ment showed decrease in the RI, while in the LTFC treat- and increased Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study
ment group the RI was increased compared to baseline. score and with reduced temporal, superior, nasal, inferior,
No statistically significant differences in the visual field temporal (TSNIT) average, reduced inferior average, and
examination or in the NFL thickness were observed be- increased nerve fiber indicator (NFI). Larger mean BP fluc-
tween the two treatment groups at baseline. Most patients tuations were associated with decreased MD, increased
showed stable visual field (Tab. III) and structural analysis PSD, and reduced TSNIT average, reduced inferior aver-
indexes (Tab. IV) during the 6- and 12-month examinations age, and increased NFI. In our study, BP was measured
in either treatment group. at the same time of day during all visits and fluctuations
between visits were statistically significant only between 6
and 12 months for systolic BP in the DTFC group. After 12
DISCUSSION months, there were no statistically significant differences in
BP and OP between the two treatment groups.
Our results show that LTFC and DTFC treatments have We found no effect of PP on visual function or structure
similar IOP-lowering effects. Overall, visual function and during 1 year of follow-up. Our findings are in agreement
structural outcome remained stable following 1 year of with a short-term study reported by Siesky et al (28) that
794
EJO_790-797_Janule.indd 794 3-08-2009 14:04:15
130