Page 707 - Accounting Principles (A Business Perspective)
P. 707
17. Analysis and interpretation of financial statements
g. Times interest earned ratio.
Solution to demonstration problem
Solution to demonstration problem A
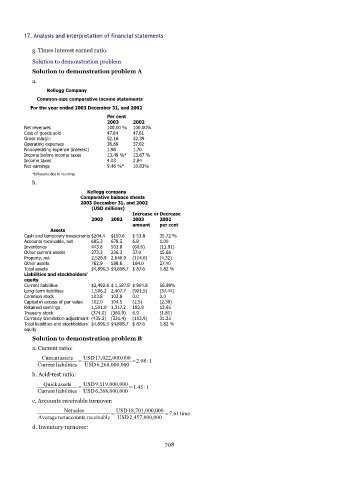
a.
Kellogg Company
Common-size comparative income statements
For the year ended 2003 December 31, and 2002
Per cent
2003 2002
Net revenues 100.00 % 100.00%
Cost of goods sold 47.84 47.61
Gross margin 52.16 52.39
Operating expenses 36.69 37.02
Nonoperating expense (interest) 1.98 1.70
Income before income taxes 13.49 %* 13.67 %
Income taxes 4.03 2.84
Net earnings 9.46 %* 10.83%
*Difference due to rounding.
b.
Kellogg company
Comparative balance sheets
2003 December 31, and 2002
(USD millions)
Increase or Decrease
2003 2002 2003 2002
amount per cent
Assets
Cash and temporary investments $204.4 $150.6 $ 53.8 35.72 %
Accounts receivable, net 685.3 678.5 6.8 1.00
Inventories 443.8 503.8 (60.0) (11.91)
Other current assets 273.3 236.3 37.0 15.66
Property, net 2,526.9 2,640.9 (114.0) (4.32)
Other assets 762.9 589.6 164.0 27.40
Total assets $4,896.3 $4,808.7 $ 87.6 1.82 %
Liabilities and stockholders'
equity
Current liabilities $2,492.6 $ 1,587.8 $ 904.8 56.98%
Long-term liabilities 1,506.2 2,407.7 (901.5) (37.44)
Common stock 103.8 103.8 0.0 0.0
Capital in excess of par value 102.0 104.5 (2.5) (2.39)
Retained earnings 1,501.0 1,317.2 183.8 13.95
Treasury stock (374.0) (380.9) 6.9 (1.81)
Currency translation adjustment (435.3) (331.4) (103.9) 31.35
Total liabilities and stockholders' $4,896.3 $4,808.7 $ 87.6 1.82 %
equity
Solution to demonstration problem B
a. Current ratio:
Currentassets USD13,022,000,000 =2.08:1
Current liabilities = USD6,268,000,000
b. Acid-test ratio:
Quickassets USD9,119,000,000 =1.45:1
Current liabilities = USD6,268,000,000
c. Accounts receivable turnover:
Netsales USD18,701,000,000
Average netaccounts receivable = USD2,457,000,000 =7.61time
d. Inventory turnover:
708