Page 25 - SSAB Welding Handbook Edition 2
P. 25
©2009-2019 by SSAB Group of companies (SSAB). All rights reserved. Only digital PDF file. No distribution. No printing allowed!
No part of this handbook may be reproduced in any form or by any means without permission in writing from SSAB.
Welding handbook 4.0 Hydrogen cracks
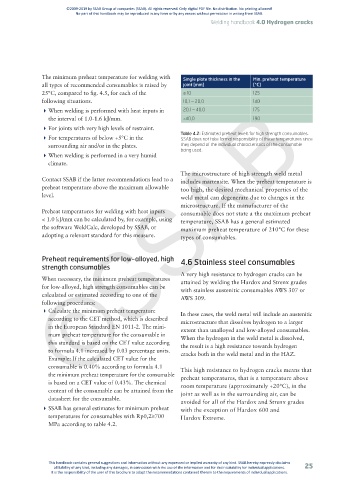
The minimum preheat temperature for welding with Single plate thickness in the Min. preheat temperature
all types of recommended consumables is raised by joint [mm] [°C]
©SSAB
25°C, compared to fig. 4.5, for each of the ≤ 10 125
following situations. 10,1 – 20,0 140
4 When welding is performed with heat inputs in 20,1 – 40,0 175
the interval of 1.0-1.6 kJ/mm. >40,0 190
4 For joints with very high levels of restraint.
Table 4.2: Estimated preheat levels for high strength consumables.
4 For temperatures of below +5°C in the SSAB does not take formal responsibility of these temperatures since
surrounding air and/or in the plates. they depend of the individual characteristics of the consumable
being used.
4 When welding is performed in a very humid
climate.
The microstructure of high strength weld metal
Contact SSAB if the latter recommendations lead to a includes martensite. When the preheat temperature is
preheat temperature above the maximum allowable too high, the desired mechanical properties of the
level. weld metal can degenerate due to changes in the
microstructure. If the manufacturer of the
Preheat temperatures for welding with heat inputs consumable does not state a the maximum preheat
< 1.0 kJ/mm can be calculated by, for example, using temperature, SSAB has a general estimated
the software WeldCalc, developed by SSAB, or maximum preheat temperature of 210°C for these
adopting a relevant standard for this measure. types of consumables.
Preheat requirements for low-alloyed, high 4.6 Stainless steel consumables
strength consumables
A very high resistance to hydrogen cracks can be
When necessary, the minimum preheat temperatures attained by welding the Hardox and Strenx grades
for low-alloyed, high strength consumables can be with stainless austenitic consumables AWS 307 or
calculated or estimated according to one of the AWS 309.
following procedures:
4 Calculate the minimum preheat temperature In these cases, the weld metal will include an austenitic
according to the CET method, which is described microstructure that dissolves hydrogen to a larger
in the European Standard EN 1011-2. The mini- extent than unalloyed and low-alloyed consumables.
mum preheat temperature for the consumable in When the hydrogen in the weld metal is dissolved,
this standard is based on the CET value according the result is a high resistance towards hydrogen
to formula 4.1 increased by 0.03 percentage units. cracks both in the weld metal and in the HAZ.
Example: If the calculated CET value for the
consumable is 0.40% according to formula 4.1 This high resistance to hydrogen cracks means that
the minimum preheat temperature for the consumable preheat temperatures, that is a temperature above
is based on a CET value of 0.43%. The chemical room temperature (approximately +20°C), in the
content of the consumable can be attained from the joint as well as in the surrounding air, can be
datasheet for the consumable.
avoided for all of the Hardox and Strenx grades
4 SSAB has general estimates for minimum preheat with the exception of Hardox 600 and
temperatures for consumables with Rp0,2≥700 Hardox Extreme.
MPa according to table 4.2.
This handbook contains general suggestions and information without any expressed or implied warranty of any kind. SSAB hereby expressly disclaims
all liability of any kind, including any damages, in connection with the use of the information and for their suitability for individual applications. 25
It is the responsibility of the user of this brochure to adapt the recommendations contained therein to the requirements of individual applications.