Page 23 - 100 Great Business Ideas: From Leading Companies Around the World (100 Great Ideas)
P. 23
1,5cape 1 1(m /lir A Id JucreasmN Pet., rlllrl ( jou! ►
taiVity Poientral ti iy,cusses how to raise personal creativity
levels by working to improve intuition and by removing
barriers to creativity. Abrief discussion of how to improve
group dynamics in order to improve group creativity is
included.
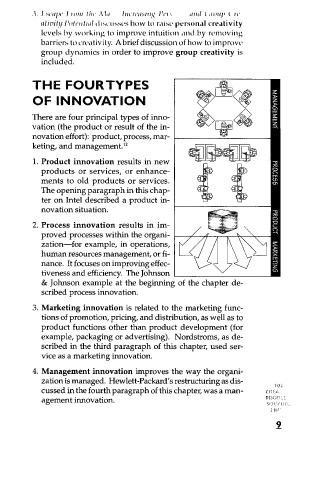
THE FOURTYPES sAteik!' .t•, 4— t1 !. v4 z>KC>)
K
OF INNOVATION tt --i
.74
There are four principal types of inno- .73
vation (the product or result of the in- .
novation effort): product, process, mar- XI
keting, and management. 12 M '4 I • C.
(-)
I. Product innovation results in new 416 rn
products or services, or enhance- cn
ments to old products or services. el lb I I— (SI
The opening paragraph in this chap-
ter on Intel described a product in- P !P '73
novation situation. 0
1OD t.'4..-o1..1.1,
rZ3
AO! 40h.Ti .F.-
C--iI
,.... K
n
2. Process innovation results in im- 7"
r-r-lI
proved processes within the organi- .-::-._•-- 2
zation—for example, in operations,
human resources management, or fi-
nance. It focuses on improving effec-
tiveness and efficiency. The Johnson
& Johnson example at the beginning of the chapter de-
scribed process innovation.
3. Marketing innovation is related to the marketing func-
tions of promotion, pricing, and distribution, as well as to
product functions other than product development (for
example, packaging or advertising). Nordstroms, as de-
scribed in the third paragraph of this chapter, used ser-
vice as a marketing innovation.
4. Management innovation improves the way the organi-
zation is managed. Hewlett-Packard's restructuring as dis-
cussed in the fourth paragraph of this chapter, was a man-
agement innovation.
9