Page 10 - E-LKM ASAM BASA
P. 10
3. Lewis Theory
According to the Lewis definition, a molecule behaves as a base
when it donates a lone pair of electrons. Conversely, a molecule
behaves as an acid when it accepts a lone pair. So while the
Brønsted–Lowry definition focuses on the action of a proton, the Lewis
definition focuses on the action of a lone pair.
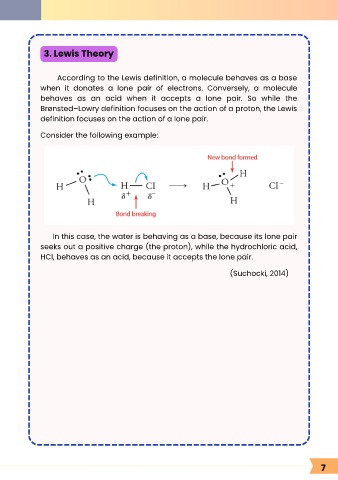
Consider the following example:
In this case, the water is behaving as a base, because its lone pair
seeks out a positive charge (the proton), while the hydrochloric acid,
HCl, behaves as an acid, because it accepts the lone pair.
(Suchocki, 2014)
7