Page 11 - E-LKM ASAM BASA
P. 11
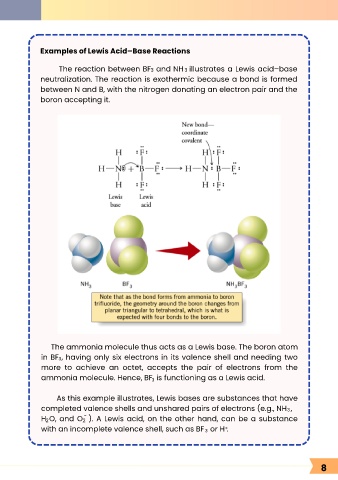
Examples of Lewis Acid–Base Reactions
The reaction between BF and NH illustrates a Lewis acid–base
3
3
neutralization. The reaction is exothermic because a bond is formed
between N and B, with the nitrogen donating an electron pair and the
boron accepting it.
The ammonia molecule thus acts as a Lewis base. The boron atom
in BF , having only six electrons in its valence shell and needing two
3
more to achieve an octet, accepts the pair of electrons from the
ammonia molecule. Hence, BF is functioning as a Lewis acid.
3
As this example illustrates, Lewis bases are substances that have
completed valence shells and unshared pairs of electrons (e.g., NH ,
3
-
H O, and O ). A Lewis acid, on the other hand, can be a substance
2
2
with an incomplete valence shell, such as BF or H .
+
3
8