Page 10 - Group 4_Project_CESP2021
P. 10
C. Based on The Electron Source
1. Covalent Coordinate Bond
Coordinate covalent bond is a covalent bond in which the electron pairs
used for bonding come from only one of the atoms. Consider the following
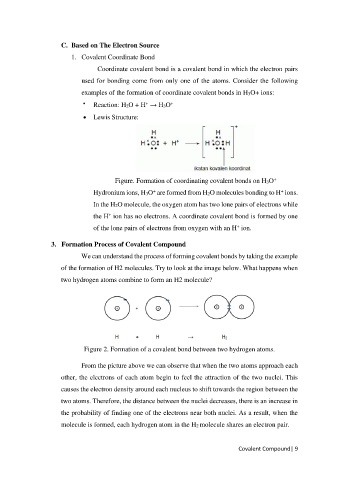
examples of the formation of coordinate covalent bonds in H3O+ ions:
+
• Reaction: H2O + H → H3O +
• Lewis Structure:
Figure. Formation of coordinating covalent bonds on H3O
+
+
+
Hydronium ions, H3O are formed from H2O molecules bonding to H ions.
In the H2O molecule, the oxygen atom has two lone pairs of electrons while
+
the H ion has no electrons. A coordinate covalent bond is formed by one
+
of the lone pairs of electrons from oxygen with an H ion.
3. Formation Process of Covalent Compound
We can understand the process of forming covalent bonds by taking the example
of the formation of H2 molecules. Try to look at the image below. What happens when
two hydrogen atoms combine to form an H2 molecule?
Figure 2. Formation of a covalent bond between two hydrogen atoms.
From the picture above we can observe that when the two atoms approach each
other, the electrons of each atom begin to feel the attraction of the two nuclei. This
causes the electron density around each nucleus to shift towards the region between the
two atoms. Therefore, the distance between the nuclei decreases, there is an increase in
the probability of finding one of the electrons near both nuclei. As a result, when the
molecule is formed, each hydrogen atom in the H2 molecule shares an electron pair.
Covalent Compound| 9