Page 37 - Demo 1
P. 37
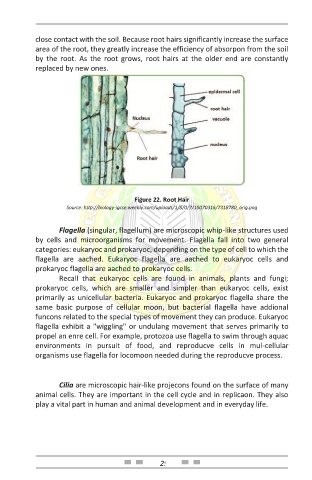
close contact with the soil. Because root hairs significantly increase the surface
area of the root, they greatly increase the efficiency of absorpon from the soil
by the root. As the root grows, root hairs at the older end are constantly
replaced by new ones.
Figure 22. Root Hair
Source: http://biology-igcse.weebly.com/uploads/1/5/0/7/15070316/7318780_orig.png
Flagella (singular, flagellum) are microscopic whip-like structures used
by cells and microorganisms for movement. Flagella fall into two general
categories: eukaryoc and prokaryoc, depending on the type of cell to which the
flagella are aached. Eukaryoc flagella are aached to eukaryoc cells and
prokaryoc flagella are aached to prokaryoc cells.
Recall that eukaryoc cells are found in animals, plants and fungi;
prokaryoc cells, which are smaller and simpler than eukaryoc cells, exist
primarily as unicellular bacteria. Eukaryoc and prokaryoc flagella share the
same basic purpose of cellular moon, but bacterial flagella have addional
funcons related to the special types of movement they can produce. Eukaryoc
flagella exhibit a "wiggling" or undulang movement that serves primarily to
propel an enre cell. For example, protozoa use flagella to swim through aquac
environments in pursuit of food, and reproducve cells in mul-cellular
organisms use flagella for locomoon needed during the reproducve process.
Cilia are microscopic hair-like projecons found on the surface of many
animal cells. They are important in the cell cycle and in replicaon. They also
play a vital part in human and animal development and in everyday life.
29