Page 638 - TaxAdviser_2022
P. 638
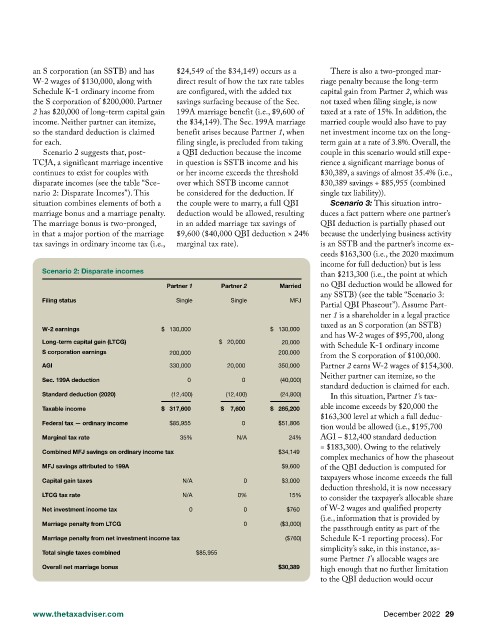
an S corporation (an SSTB) and has $24,549 of the $34,149) occurs as a There is also a two-pronged mar-
W-2 wages of $130,000, along with direct result of how the tax rate tables riage penalty because the long-term
Schedule K-1 ordinary income from are configured, with the added tax capital gain from Partner 2, which was
the S corporation of $200,000. Partner savings surfacing because of the Sec. not taxed when filing single, is now
2 has $20,000 of long-term capital gain 199A marriage benefit (i.e., $9,600 of taxed at a rate of 15%. In addition, the
income. Neither partner can itemize, the $34,149). The Sec. 199A marriage married couple would also have to pay
so the standard deduction is claimed benefit arises because Partner 1, when net investment income tax on the long-
for each. filing single, is precluded from taking term gain at a rate of 3.8%. Overall, the
Scenario 2 suggests that, post- a QBI deduction because the income couple in this scenario would still expe-
TCJA, a significant marriage incentive in question is SSTB income and his rience a significant marriage bonus of
continues to exist for couples with or her income exceeds the threshold $30,389, a savings of almost 35.4% (i.e.,
disparate incomes (see the table “Sce- over which SSTB income cannot $30,389 savings ÷ $85,955 (combined
nario 2: Disparate Incomes”). This be considered for the deduction. If single tax liability)).
situation combines elements of both a the couple were to marry, a full QBI Scenario 3: This situation intro-
marriage bonus and a marriage penalty. deduction would be allowed, resulting duces a fact pattern where one partner’s
The marriage bonus is two-pronged, in an added marriage tax savings of QBI deduction is partially phased out
in that a major portion of the marriage $9,600 ($40,000 QBI deduction × 24% because the underlying business activity
tax savings in ordinary income tax (i.e., marginal tax rate). is an SSTB and the partner’s income ex-
ceeds $163,300 (i.e., the 2020 maximum
income for full deduction) but is less
Scenario 2: Disparate incomes
than $213,300 (i.e., the point at which
Partner 1 Partner 2 Married no QBI deduction would be allowed for
any SSTB) (see the table “Scenario 3:
Filing status Single Single MFJ
Partial QBI Phaseout”). Assume Part-
ner 1 is a shareholder in a legal practice
W-2 earnings $ 130,000 $ 130,000 taxed as an S corporation (an SSTB)
and has W-2 wages of $95,700, along
Long-term capital gain (LTCG) $ 20,000 20,000 with Schedule K-1 ordinary income
S corporation earnings 200,000 200,000
from the S corporation of $100,000.
AGI 330,000 20,000 350,000 Partner 2 earns W-2 wages of $154,300.
Sec. 199A deduction 0 0 (40,000) Neither partner can itemize, so the
standard deduction is claimed for each.
Standard deduction (2020) (12,400) (12,400) (24,800) In this situation, Partner 1’s tax-
Taxable income $ 317,600 $ 7,600 $ 285,200 able income exceeds by $20,000 the
$163,300 level at which a full deduc-
Federal tax — ordinary income $85,955 0 $51,806
tion would be allowed (i.e., $195,700
Marginal tax rate 35% N/A 24% AGI – $12,400 standard deduction
= $183,300). Owing to the relatively
Combined MFJ savings on ordinary income tax $34,149
complex mechanics of how the phaseout
MFJ savings attributed to 199A $9,600 of the QBI deduction is computed for
Capital gain taxes N/A 0 $3,000 taxpayers whose income exceeds the full
deduction threshold, it is now necessary
LTCG tax rate N/A 0% 15%
to consider the taxpayer’s allocable share
Net investment income tax 0 0 $760 of W-2 wages and qualified property
(i.e., information that is provided by
Marriage penalty from LTCG 0 ($3,000)
the passthrough entity as part of the
Marriage penalty from net investment income tax ($760) Schedule K-1 reporting process). For
Total single taxes combined $85,955 simplicity’s sake, in this instance, as-
sume Partner 1’s allocable wages are
Overall net marriage bonus $30,389 high enough that no further limitation
to the QBI deduction would occur
www.thetaxadviser.com December 2022 29