Page 54 - e-CPG-SLE-8_5_24
P. 54
Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Oral contraceptive and intrauterine device (IUD) have no association
with thrombosis, worsening of SLEDAI score and mortality in patients
with SLE. 15, level I; 109, level I Refer to Appendix 10 for the Types of
Contraception Recommended for Patients with SLE.
Recommendation 12
• All women with systemic lupus erythematosus in the reproductive
age should receive pre-pregnancy counselling.
b. Antenatal care
The management principles for SLE during pregnancy are as follows:
• Obstetric Care: Standard pregnancy care protocols provided by
the obstetric team shall be followed.
• Rheumatological or Subspecialty Care: The rheumatologist
or a subspecialty team will co-manage any disease-related
complications and ensure optimal care for the patient.
• Combined Care: Effective communication and multidisciplinary
care among healthcare providers co-ordinated by family medicine
specialists are essential.
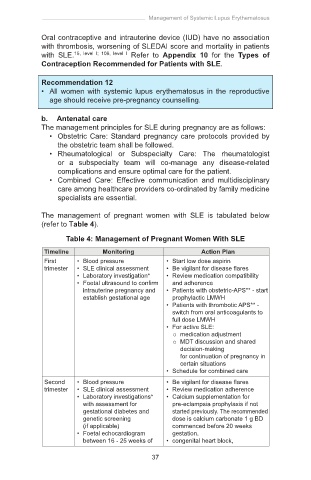
The management of pregnant women with SLE is tabulated below
(refer to Table 4).
Table 4: Management of Pregnant Women With SLE
Timeline Monitoring Action Plan
First • Blood pressure • Start low dose aspirin
trimester • SLE clinical assessment • Be vigilant for disease flares
• Laboratory investigation* • Review medication compatibility
• Foetal ultrasound to confirm and adherence
intrauterine pregnancy and • Patients with obstetric-APS** - start
establish gestational age prophylactic LMWH
• Patients with thrombotic APS** -
switch from oral anticoagulants to
full dose LMWH
• For active SLE:
medication adjustment
MDT discussion and shared
decision-making
for continuation of pregnancy in
certain situations
• Schedule for combined care
Second • Blood pressure • Be vigilant for disease flares
trimester • SLE clinical assessment • Review medication adherence
• Laboratory investigations* • Calcium supplementation for
with assessment for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis if not
gestational diabetes and started previously. The recommended
genetic screening dose is calcium carbonate 1 g BD
(if applicable) commenced before 20 weeks
• Foetal echocardiogram gestation.
between 16 - 25 weeks of • congenital heart block,
37
gestation for mothers with co-management with feto-maternal
positive anti-Ro/SSA or specialist is required
anti-La/SSB by feto-maternal
specialist
• Ultrasound to evaluate foetal
anatomy, foetal growth and
placental insufficiency
Third • Blood pressure • Be vigilant for disease flares
trimester • SLE clinical assessment • Review medication adherence
• Laboratory investigations* • Review preparations for labour and
• Regular ultrasound to delivery
evaluate foetal growth, • Avoid NSAIDs
adequacy of amniotic fluid
and placental insufficiency
Post- • Blood pressure • Be vigilant for disease flares
partum and • SLE clinical assessment • For APS - continue LMWH for
lactation • Laboratory investigations* 6 weeks
• Switch to lactation compatible
medications if breastfeeding is
desired
• For prednisolone ≥40 mg/day,
delay breastfeeding at least four
hours after consumption
• Refer neonate to paediatrician to
rule out neonatal lupus
• Advise regarding contraception***