Page 58 - e-CPG-SLE-8_5_24
P. 58
Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
10.5 Vaccination
Vaccination is an important strategy in patients with SLE as they are
susceptible to infection due to the disease itself, immunosuppressive
therapy and presence of co-morbidities. EULAR recommends annual
assessment of vaccination status of patients with autoimmune
inflammatory rheumatic diseases and administration of vaccines
during quiescent disease. 121
The evidence for effectiveness based on immunogenicity and safety
for vaccines in SLE patients are provided in the table below (refer to
Table 5).
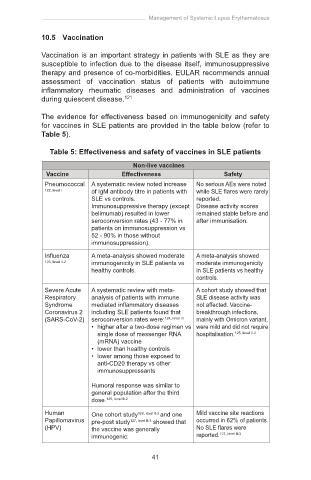
Table 5: Effectiveness and safety of vaccines in SLE patients
Non-live vaccines
Vaccine Effectiveness Safety
Pneumococcal A systematic review noted increase No serious AEs were noted
122, level I of IgM antibody titre in patients with while SLE flares were rarely
SLE vs controls. reported.
Immunosuppressive therapy (except Disease activity scores
belimumab) resulted in lower remained stable before and
seroconversion rates (43 - 77% in after immunisation.
patients on immunosuppression vs
52 - 90% in those without
immunosuppression).
Influenza A meta-analysis showed moderate A meta-analysis showed
123, level II-2 immunogenicity in SLE patients vs moderate immunogenicity
healthy controls. in SLE patients vs healthy
controls.
Severe Acute A systematic review with meta- A cohort study showed that
Respiratory analysis of patients with immune SLE disease activity was
Syndrome mediated inflammatory diseases not affected. Vaccine-
Coronavirus 2 including SLE patients found that breakthrough infections,
(SARS-CoV-2) seroconversion rates were: 124, level III mainly with Omicron variant,
• higher after a two-dose regimen vs were mild and did not require
single dose of messenger RNA hospitalisation. 125, level II-2
(mRNA) vaccine
• lower than healthy controls
• lower among those exposed to
anti-CD20 therapy vs other
immunosuppressants
Humoral response was similar to
general population after the third
dose. 125, level II-2
Human One cohort study 126, level II-2 and one Mild vaccine site reactions
Papillomavirus pre-post study 127, level II-3 showed that occurred in 62% of patients.
(HPV) the vaccine was generally No SLE flares were
immunogenic: reported. 127, level II-3
41
• seroconversion was 100% for those
seronegative at baseline 127, level II-3
• high rate of immunogenicity was
retained at five years in stable
patients 126, level II-2
Live vaccines
Herpes Zoster The vaccine induces humoral and Safe and well-tolerated in
(HZ) 128, level I cell-mediated response in stable stable patients not
SLE patients not receiving intensive receiving intensive
immunosuppressive therapies. immunosuppression. No
differences noted in AEs
except for injection site
reactions in vaccine-
treated patients vs those
on placebo. Low number
of SLE flares were noted in
both groups.