Page 59 - e-CPG-SLE-8_5_24
P. 59
Non-live vaccines
Vaccine
Effectiveness
Safety
Pneumococcal
of IgM antibody titre in patients with
while SLE flares were rarely
122, level I
reported.
SLE vs controls.
Immunosuppressive therapy (except
Disease activity scores
remained stable before and
belimumab) resulted in lower
after immunisation.
seroconversion rates (43 - 77% in
patients on immunosuppression vs
52 - 90% in those without
immunosuppression).
A meta-analysis showed moderate
Influenza
A meta-analysis showed
moderate immunogenicity
immunogenicity in SLE patients vs
123, level II-2
healthy controls.
in SLE patients vs healthy
controls.
A cohort study showed that
A systematic review with meta-
Severe Acute
analysis of patients with immune
SLE disease activity was
Respiratory
not affected. Vaccine-
Syndrome
mediated inflammatory diseases
including SLE patients found that
breakthrough infections,
Coronavirus 2
mainly with Omicron variant,
(SARS-CoV-2)
seroconversion rates were:
124, level III
• higher after a two-dose regimen vs were mild and did not require
hospitalisation.
single dose of messenger RNA
125, level II-2
(mRNA) vaccine
• lower than healthy controls
• lower among those exposed to
anti-CD20 therapy vs other
immunosuppressants
Humoral response was similar to
general population after the third
dose.
125, level II-2
Human
Mild vaccine site reactions
One cohort study
and one
126, level II-2
occurred in 62% of patients.
Papillomavirus
pre-post study
showed that
127, level II-3
(HPV) A systematic review noted increase No serious AEs were noted
No SLE flares were
the vaccine was generally
immunogenic: reported. 127, level II-3
Management of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
• seroconversion was 100% for those
seronegative at baseline 127, level II-3
• high rate of immunogenicity was
retained at five years in stable
patients 126, level II-2
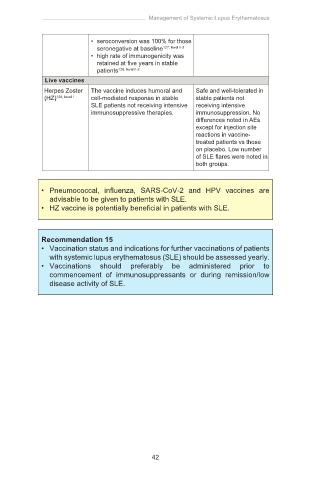
Live vaccines
Herpes Zoster The vaccine induces humoral and Safe and well-tolerated in
(HZ) 128, level I cell-mediated response in stable stable patients not
SLE patients not receiving intensive receiving intensive
immunosuppressive therapies. immunosuppression. No
differences noted in AEs
except for injection site
reactions in vaccine-
treated patients vs those
on placebo. Low number
of SLE flares were noted in
both groups.
• Pneumococcal, influenza, SARS-CoV-2 and HPV vaccines are
advisable to be given to patients with SLE.
• HZ vaccine is potentially beneficial in patients with SLE.
Recommendation 15
• Vaccination status and indications for further vaccinations of patients
with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) should be assessed yearly.
• Vaccinations should preferably be administered prior to
commencement of immunosuppressants or during remission/low
disease activity of SLE.
42