Page 333 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 333
300 SECTION | II Organ Toxicity
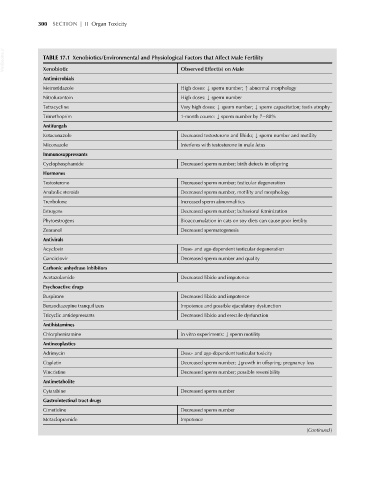
VetBooks.ir TABLE 17.1 Xenobiotics/Environmental and Physiological Factors that Affect Male Fertility
Observed Effect(s) on Male
Xenobiotic
Antimicrobials
Metronidazole High doses: k sperm number; m abnormal morphology
Nitrofurantoin High doses: k sperm number
Tetracycline Very high doses: k sperm number; k sperm capacitation; testis atrophy
Trimethoprim 1-month course: k sperm number by 7 88%
Antifungals
Ketaconazole Decreased testosterone and libido; k sperm number and motility
Miconazole Interferes with testosterone in male fetus
Immunosuppressants
Cyclophosphamide Decreased sperm number; birth defects in offspring
Hormones
Testosterone Decreased sperm number; testicular degeneration
Anabolic steroids Decreased sperm number, motility and morphology
Trenbolone Increased sperm abnormalities
Estrogens Decreased sperm number; behavioral feminization
Phytoestrogens Bioaccumulation in cats on soy diets can cause poor fertility
Zearanol Decreased spermatogenesis
Antivirals
Acyclovir Dose- and age-dependent testicular degeneration
Ganciclovir Decreased sperm number and quality
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Acetazolamide Decreased libido and impotence
Psychoactive drugs
Buspirone Decreased libido and impotence
Benzodiazepine tranquilizers Impotence and possible ejaculatory dysfunction
Tricyclic antidepressants Decreased libido and erectile dysfunction
Antihistamines
Chlorpheniramine In vitro experiments: k sperm motility
Antineoplastics
Adrimycin Dose- and age-dependent testicular toxicity
Cisplatin Decreased sperm number; kgrowth in offspring; pregnancy loss
Vincristine Decreased sperm number; possible reversibility
Antimetabolite
Cytarabine Decreased sperm number
Gastrointestinal tract drugs
Cimetidine Decreased sperm number
Metaclopramide Impotence
(Continued )