Page 576 - The Toxicology of Fishes
P. 576
556 The Toxicology of Fishes
EGF
Cell-cycle stage
G 0
Cell membrane
G 1 Cytoplasm
GDP
Inactive ras GTP
Active ras
P P
Grb2
SoS1
Nucleus
Raf I
Rb Pi
P P MEK/
Pi MAPKK
Pi
Early response Active
gene activation MAPK MAPK
Transcription E2F Rb
factor
Inactive Active
Pi
Pi
RNA and protein
G 1 synthesis
S DNA synthesis
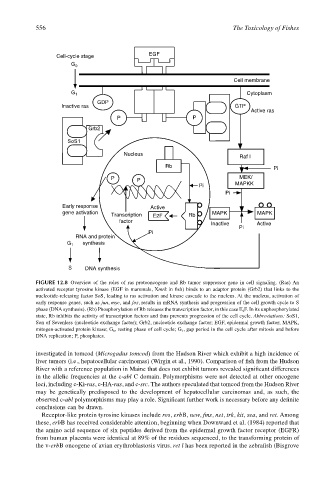
FIGURE 12.8 Overview of the roles of ras protooncogene and Rb tumor suppressor gene in cell signaling. (Ras) An
activated receptor tyrosine kinase (EGF in mammals, Xmrk in fish) binds to an adaptor protein (Grb2) that links to the
nucleotide-releasing factor SoS, leading to ras activation and kinase cascade to the nucleus. At the nucleus, activation of
early response genes, such as jun, myc, and fos, results in mRNA synthesis and progression of the cell growth cycle to S
phase (DNA synthesis). (Rb) Phosphorylation of Rb releases the transcription factor, in this case E 2 F. In its unphosphorylated
state, Rb inhibits the activity of transcription factors and thus prevents progression of the cell cycle. Abbreviations: SoS1,
Son of Sevenless (nucleotide exchange factor); Grb2, nucleotide exchange factor; EGF, epidermal growth factor; MAPK,
mitogen-activated protein kinase; G 0 , resting phase of cell cycle; G 1 , gap period in the cell cycle after mitosis and before
DNA replication; P, phosphates.
investigated in tomcod (Microgadus tomcod) from the Hudson River which exhibit a high incidence of
liver tumors (i.e., hepatocellular carcinomas) (Wirgin et al., 1990). Comparison of fish from the Hudson
River with a reference population in Maine that does not exhibit tumors revealed significant differences
in the allelic frequencies at the c-abl C domain. Polymorphisms were not detected at other oncogene
loci, including c-Ki-ras, c-HA-ras, and c-src. The authors speculated that tomcod from the Hudson River
may be genetically predisposed to the development of hepatocellular carcinomas and, as such, the
observed c-abl polymorphisms may play a role. Significant further work is necessary before any definite
conclusions can be drawn.
Receptor-like protein tyrosine kinases include ros, erbB, new, fms, net, trk, kit, sea, and ret. Among
these, erbB has received considerable attention, beginning when Downward et al. (1984) reported that
the amino acid sequence of six peptides derived from the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)
from human placenta were identical at 89% of the residues sequenced, to the transforming protein of
the v-erbB oncogene of avian erythroblastosis virus. ret l has been reported in the zebrafish (Bisgrove