Page 572 - The Toxicology of Fishes
P. 572
552 The Toxicology of Fishes
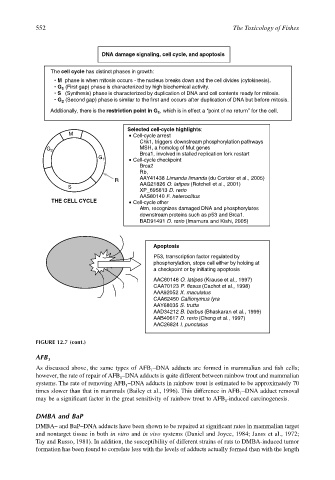
DNA damage signaling, cell cycle, and apoptosis
The cell cycle has distinct phases in growth:
• M phase is when mitosis occurs - the nucleus breaks down and the cell divides (cytokinesis).
• G 1 (First gap) phase is characterized by high biochemical activity.
• S (Synthesis) phase is characterized by duplication of DNA and cell contents ready for mitosis.
• G (Second gap) phase is similar to the first and occurs after duplication of DNA but before mitosis.
2
Additionally, there is the restriction point in G , which is in effect a “point of no returnʼʼ for the cell.
1
Selected cell-cycle highlights:
M Cell-cycle arrest
Chk1, triggers downstream phosphorylation pathways
G 2 MSH, a homolog of Mut genes
Brca1, involved in stalled replication fork restart
G 1 Cell-cycle checkpoint
Brca2
Rb,
R AAY41438 Limanda limanda (du Corbier et al., 2005)
S AAG21826 O. latipes (Rotchell et al., 2001)
XP_695613 D. rerio
AAS80140 F. heteroclitus
THE CELL CYCLE Cell-cycle other
Atm, recognizes damaged DNA and phosphorylates
downstream proteins such as p53 and Brca1.
BAD91491 D. rerio (Imamura and Kishi, 2005)
Apoptosis
P53, transcription factor regulated by
phosphorylation, stops cell either by holding at
a checkpoint or by initiating apoptosis
AAC60146 O. latipes (Krause et al., 1997)
CAA70123 P. flesus (Cachot et al., 1998)
AAA92052 X. maculatus
CAA62450 Callionymus lyra
AAY68035 S. trutta
AAD34212 B. barbus (Bhaskaran et al., 1999)
AAB40617 D. rerio (Cheng et al., 1997)
AAC26824 I. punctatus
FIGURE 12.7 (cont.)
AFB 1
As discussed above, the same types of AFB –DNA adducts are formed in mammalian and fish cells;
1
however, the rate of repair of AFB –DNA adducts is quite different between rainbow trout and mammalian
1
systems. The rate of removing AFB –DNA adducts in rainbow trout is estimated to be approximately 70
1
times slower than that in mammals (Bailey et al., 1996). This difference in AFB –DNA adduct removal
1
may be a significant factor in the great sensitivity of rainbow trout to AFB -induced carcinogenesis.
1
DMBA and BaP
DMBA– and BaP–DNA adducts have been shown to be repaired at significant rates in mammalian target
and nontarget tissue in both in vitro and in vivo systems (Daniel and Joyce, 1984; Janss et al., 1972;
Tay and Russo, 1981). In addition, the susceptibility of different strains of rats to DMBA-induced tumor
formation has been found to correlate less with the levels of adducts actually formed than with the length