Page 570 - The Toxicology of Fishes
P. 570
550 The Toxicology of Fishes
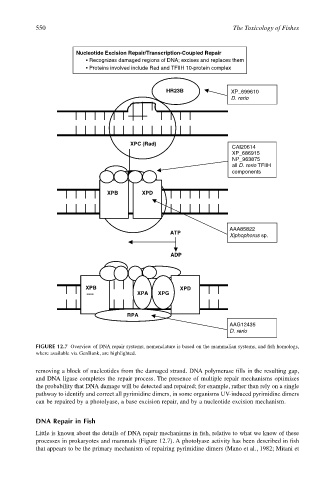
Nucleotide Excision Repair/Transcription-Coupled Repair
Recognizes damaged regions of DNA; excises and replaces them
Proteins involved include Rad and TFIIH 10-protein complex
HR23B XP_699610
D. rerio
XPC (Rad)
CAI20614
XP_686915
NP_963875
all D. rerio TFIIH
components
XPB XPD
AAA85822
ATP
Xiphophorus sp.
ADP
XPB XPD
---- XPA XPG
RPA
AAG12435
D. rerio
FIGURE 12.7 Overview of DNA repair systems; nomenclature is based on the mammalian systems, and fish homologs,
where available via GenBank, are highlighted.
removing a block of nucleotides from the damaged strand. DNA polymerase fills in the resulting gap,
and DNA ligase completes the repair process. The presence of multiple repair mechanisms optimizes
the probability that DNA damage will be detected and repaired; for example, rather than rely on a single
pathway to identify and correct all pyrimidine dimers, in some organisms UV-induced pyrimidine dimers
can be repaired by a photolyase, a base excision repair, and by a nucleotide excision mechanism.
DNA Repair in Fish
Little is known about the details of DNA repair mechanisms in fish, relative to what we know of these
processes in prokaryotes and mammals (Figure 12.7). A photolyase activity has been described in fish
that appears to be the primary mechanism of repairing pyrimidine dimers (Mano et al., 1982; Mitani et