Page 640 - The Toxicology of Fishes
P. 640
620 The Toxicology of Fishes
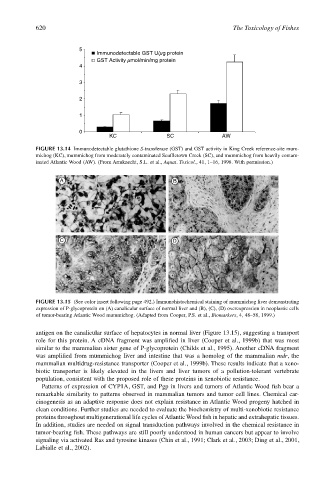
5
Immunodetectable GST U/µg protein
GST Activity µmol/min/mg protein
4
3
2
1
0
KC SC AW
FIGURE 13.14 Immunodetectable glutathione S-transferase (GST) and GST activity in King Creek reference-site mum-
michog (KC), mummichog from moderately contaminated Scuffletown Creek (SC), and mummichog from heavily contam-
inated Atlantic Wood (AW). (From Armknecht, S.L. et al., Aquat. Toxicol., 41, 1–16, 1998. With permission.)
A B
C D
FIGURE 13.15 (See color insert following page 492.) Immunohistochemical staining of mummichog liver demonstrating
expression of P-glycoprotein on (A) canalicular surface of normal liver and (B), (C), (D) overexpression in neoplastic cells
of tumor-bearing Atlantic Wood mummichog. (Adapted from Cooper, P.S. et al., Biomarkers, 4, 48–58, 1999.)
antigen on the canalicular surface of hepatocytes in normal liver (Figure 13.15), suggesting a transport
role for this protein. A cDNA fragment was amplified in liver (Cooper et al., 1999b) that was most
similar to the mammalian sister gene of P-glycoprotein (Childs et al., 1995). Another cDNA fragment
was amplified from mummichog liver and intestine that was a homolog of the mammalian mdr, the
mammalian multidrug-resistance transporter (Cooper et al., 1999b). These results indicate that a xeno-
biotic transporter is likely elevated in the livers and liver tumors of a pollution-tolerant vertebrate
population, consistent with the proposed role of these proteins in xenobiotic resistance.
Patterns of expression of CYP1A, GST, and Pgp in livers and tumors of Atlantic Wood fish bear a
remarkable similarity to patterns observed in mammalian tumors and tumor cell lines. Chemical car-
cinogenesis as an adaptive response does not explain resistance in Atlantic Wood progeny hatched in
clean conditions. Further studies are needed to evaluate the biochemistry of multi-xenobiotic resistance
proteins throughout multigenerational life cycles of Atlantic Wood fish in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues.
In addition, studies are needed on signal transduction pathways involved in the chemical resistance in
tumor-bearing fish. These pathways are still poorly understood in human cancers but appear to involve
signaling via activated Ras and tyrosine kinases (Chin et al., 1991; Clark et al., 2003; Ding et al., 2001,
Labialle et al., 2002).