Page 255 - Feline Cardiology
P. 255
262 Section G: Congestive Heart Failure
Mitral Start coronary arteries by concentric hypertrophy and/or
Aortic Valve End of Atrial Mitral increased left ventricular filling pressure (Shyu et al.
Valve Opening Rapid Systole Valve 2002; Kyriakidis et al. 1997; Cannon et al. 1985). ATP
Closure Ventricular Closure
Filling hydrolysis is required for several stages of the relaxation
process, including dissociation of actin and myosin,
QRS T QRS T
ECG P calcium dissociation from troponin C, and sequestra-
150 tion of calcium by SERCA into the sarcoplasmic reticu-
lum. Ischemia leads to greater cytosolic ADP and less
LV Pressure 100 ATP, which prolongs relaxation (as well as impairs sys-
(mmHg) tolic function). In summary, impaired relaxation is
50
caused by altered calcium handling due to abnormal
0 SERCA activity or level, enhanced myofilament sensitiv-
ity to calcium, or myocardial ischemia. Impaired or
10 delayed relaxation not only negatively impacts early
LV Volume 5 diastole, but increases myocardial stiffness through the
(ml) 0 continuing interaction of contractile elements and per-
sistent development of myocardial tension (Grossman
Congestive Heart Failure LV dv/dt –400 0 ventricular mass and myocardial composition. Stiffness
and Barry 1980).
Ventricular compliance is determined by extent of
400
is the inverse of compliance. Myocardial determinants
(ml/sec)
of stiffness include changes in the extracellular matrix
Atrial
Rapid Diastasis
Isovolumic
(titin) and myofilaments. The main component of the
Ventricular
Relaxation
cardiac extracellular matrix is collagen (Types I and III).
Filling Systole composition or isoform switches in cytoskeletal proteins
Type I collagen has the tensile strength of steel and is
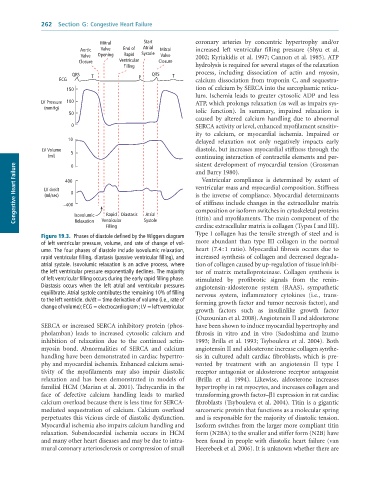
Figure 19.3. Phases of diastole defined by the Wiggers diagram
of left ventricular pressure, volume, and rate of change of vol- more abundant than type III collagen in the normal
ume. The four phases of diastole include isovolumic relaxation, heart (7.4 : 1 ratio). Myocardial fibrosis occurs due to
rapid ventricular filling, diastasis (passive ventricular filling), and increased synthesis of collagen and decreased degrada-
atrial systole. Isovolumic relaxation is an active process, where tion of collagen caused by up-regulation of tissue inhibi-
the left ventricular pressure exponentially declines. The majority tor of matrix metalloproteinase. Collagen synthesis is
of left ventricular filling occurs during the early rapid filling phase. stimulated by profibrotic signals from the renin-
Diastasis occurs when the left atrial and ventricular pressures angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), sympathetic
equilibrate. Atrial systole contributes the remaining 10% of filling nervous system, inflammatory cytokines (i.e., trans-
to the left ventricle. dv/dt = time derivative of volume (i.e., rate of forming growth factor and tumor necrosis factor), and
change of volume); ECG = electrocardiogram ; LV = left ventricular.
growth factors such as insulinlike growth factor
(Ouzounian et al. 2008). Angiotensin II and aldosterone
SERCA or increased SERCA inhibitory protein (phos- have been shown to induce myocardial hypertrophy and
pholamban) leads to increased cytosolic calcium and fibrosis in vitro and in vivo (Sadoshima and Izumo
inhibition of relaxation due to the continued actin- 1993; Brilla et al. 1993; Tsybouleva et al. 2004). Both
myosin bond. Abnormalities of SERCA and calcium angiotensin II and aldosterone increase collagen synthe-
handling have been demonstrated in cardiac hypertro- sis in cultured adult cardiac fibroblasts, which is pre-
phy and myocardial ischemia. Enhanced calcium sensi- vented by treatment with an angiotensin II type I
tivity of the myofilaments may also impair diastolic receptor antagonist or aldosterone receptor antagonist
relaxation and has been demonstrated in models of (Brilla et al. 1994). Likewise, aldosterone increases
familial HCM (Marian et al. 2001). Tachycardia in the hypertrophy in rat myocytes, and increases collagen and
face of defective calcium handling leads to marked transforming growth factor–β1 expression in rat cardiac
calcium overload because there is less time for SERCA- fibroblasts (Tsybouleva et al. 2004). Titin is a gigantic
mediated sequestration of calcium. Calcium overload sarcomeric protein that functions as a molecular spring
perpetuates this vicious circle of diastolic dysfunction. and is responsible for the majority of diastolic tension.
Myocardial ischemia also impairs calcium handling and Isoform switches from the larger more compliant titin
relaxation. Subendocardial ischemia occurs in HCM form (N2BA) to the smaller and stiffer form (N2B) have
and many other heart diseases and may be due to intra- been found in people with diastolic heart failure (van
mural coronary arteriosclerosis or compression of small Heerebeek et al. 2006). It is unknown whether there are