Page 91 - Feline Cardiology
P. 91
Chapter 10: Congenital Heart Malformations 89
Arrhythmias including occasional atrial or ventricular
premature beats may be observed.
Radiography
Depending on the severity of the defect and the age of
the cat, the radiographs may be normal or may exhibit
left-sided (atrial and/or ventricular) or generalized car-
LA diomegaly. Evidence of heart failure with patchy pulmo-
nary edema and pulmonary venous congestion may be
observed. In some cases, pulmonary artery congestion Congenital Heart Disease
may be observed, suggesting the development of pulmo-
nary hypertension.
Echocardiography
Two-dimensional echocardiography should identify the
abnormal, thickened appearance and movement of the
mitral valve. Left atrial and ventricular dilation can be
observed if the degree of dysplasia and valve regurgita-
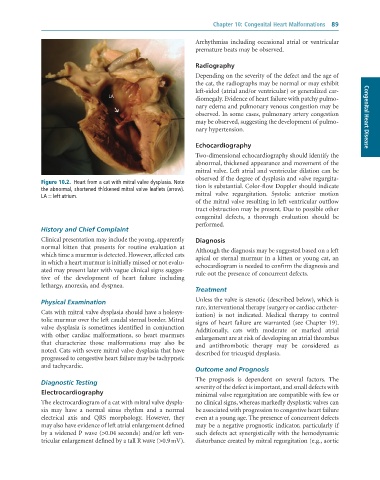
Figure 10.2. Heart from a cat with mitral valve dysplasia. Note tion is substantial. Color-flow Doppler should indicate
the abnormal, shortened thickened mitral valve leaflets (arrow). mitral valve regurgitation. Systolic anterior motion
LA = left atrium.
of the mitral valve resulting in left ventricular outflow
tract obstruction may be present. Due to possible other
congenital defects, a thorough evaluation should be
performed.
History and Chief Complaint
Clinical presentation may include the young, apparently Diagnosis
normal kitten that presents for routine evaluation at Although the diagnosis may be suggested based on a left
which time a murmur is detected. However, affected cats apical or sternal murmur in a kitten or young cat, an
in which a heart murmur is initially missed or not evalu- echocardiogram is needed to confirm the diagnosis and
ated may present later with vague clinical signs sugges- rule out the presence of concurrent defects.
tive of the development of heart failure including
lethargy, anorexia, and dyspnea.
Treatment
Unless the valve is stenotic (described below), which is
Physical Examination
rare, interventional therapy (surgery or cardiac catheter-
Cats with mitral valve dysplasia should have a holosys- ization) is not indicated. Medical therapy to control
tolic murmur over the left caudal sternal border. Mitral signs of heart failure are warranted (see Chapter 19).
valve dysplasia is sometimes identified in conjunction Additionally, cats with moderate or marked atrial
with other cardiac malformations, so heart murmurs enlargement are at risk of developing an atrial thrombus
that characterize those malformations may also be and antithrombotic therapy may be considered as
noted. Cats with severe mitral valve dysplasia that have described for tricuspid dysplasia.
progressed to congestive heart failure may be tachypneic
and tachycardic.
Outcome and Prognosis
The prognosis is dependent on several factors. The
Diagnostic Testing
severity of the defect is important, and small defects with
Electrocardiography minimal valve regurgitation are compatible with few or
The electrocardiogram of a cat with mitral valve dyspla- no clinical signs, whereas markedly dysplastic valves can
sia may have a normal sinus rhythm and a normal be associated with progression to congestive heart failure
electrical axis and QRS morphology. However, they even at a young age. The presence of concurrent defects
may also have evidence of left atrial enlargement defined may be a negative prognostic indicator, particularly if
by a widened P wave (>0.04 seconds) and/or left ven- such defects act synergistically with the hemodynamic
tricular enlargement defined by a tall R wave (>0.9 mV). disturbance created by mitral regurgitation (e.g., aortic