Page 96 - Feline Cardiology
P. 96
94 Section C: Congenital Heart Disease
RA
Congenital Heart Disease LA
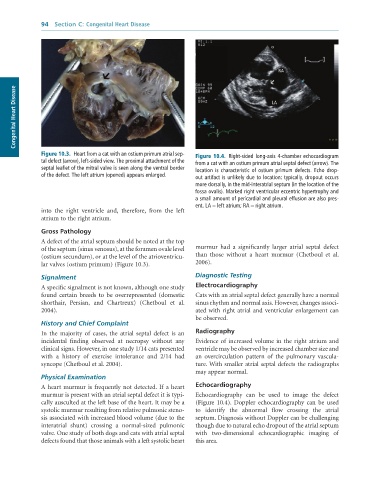
Figure 10.3. Heart from a cat with an ostium primum atrial sep- Figure 10.4. Right-sided long-axis 4-chamber echocardiogram
tal defect (arrow), left-sided view. The proximal attachment of the
from a cat with an ostium primum atrial septal defect (arrow). The
septal leaflet of the mitral valve is seen along the ventral border location is characteristic of ostium primum defects. Echo drop-
of the defect. The left atrium (opened) appears enlarged.
out artifact is unlikely due to location: typically, dropout occurs
more dorsally, in the mid-interatrial septum (in the location of the
fossa ovalis). Marked right ventricular eccentric hypertrophy and
a small amount of pericardial and pleural effusion are also pres-
ent. LA = left atrium; RA = right atrium.
into the right ventricle and, therefore, from the left
atrium to the right atrium.
Gross Pathology
A defect of the atrial septum should be noted at the top
of the septum (sinus venosus), at the foramen ovale level murmur had a significantly larger atrial septal defect
(ostium secundum), or at the level of the atrioventricu- than those without a heart murmur (Chetboul et al.
lar valves (ostium primum) (Figure 10.3). 2006).
Signalment Diagnostic Testing
A specific signalment is not known, although one study Electrocardiography
found certain breeds to be overrepresented (domestic Cats with an atrial septal defect generally have a normal
shorthair, Persian, and Chartreux) (Chetboul et al. sinus rhythm and normal axis. However, changes associ-
2004). ated with right atrial and ventricular enlargement can
be observed.
History and Chief Complaint
In the majority of cases, the atrial septal defect is an Radiography
incidental finding observed at necropsy without any Evidence of increased volume in the right atrium and
clinical signs. However, in one study 1/14 cats presented ventricle may be observed by increased chamber size and
with a history of exercise intolerance and 2/14 had an overcirculation pattern of the pulmonary vascula-
syncope (Chetboul et al. 2004). ture. With smaller atrial septal defects the radiographs
may appear normal.
Physical Examination
A heart murmur is frequently not detected. If a heart Echocardiography
murmur is present with an atrial septal defect it is typi- Echocardiography can be used to image the defect
cally ausculted at the left base of the heart. It may be a (Figure 10.4). Doppler echocardiography can be used
systolic murmur resulting from relative pulmonic steno- to identify the abnormal flow crossing the atrial
sis associated with increased blood volume (due to the septum. Diagnosis without Doppler can be challenging
interatrial shunt) crossing a normal-sized pulmonic though due to natural echo dropout of the atrial septum
valve. One study of both dogs and cats with atrial septal with two-dimensional echocardiographic imaging of
defects found that those animals with a left systolic heart this area.