Page 149 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 149
116 SECTION | I General
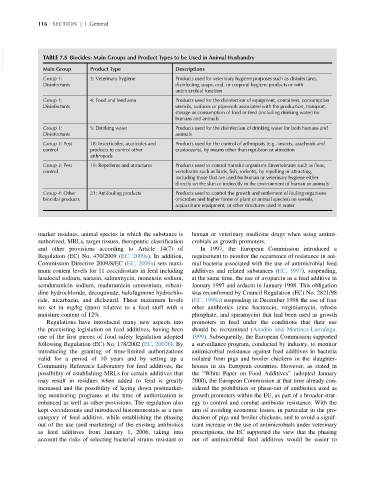
VetBooks.ir TABLE 7.5 Biocides: Main Groups and Product Types to be Used in Animal Husbandry
Main Group
Descriptions
Product Type
Group 1: 3: Veterinary hygiene Products used for veterinary hygiene purposes such as disinfectants,
Disinfectants disinfecting soaps, oral, or corporal hygiene products or with
antimicrobial function
Group 1: 4: Food and feed area Products used for the disinfection of equipment, containers, consumption
Disinfectants utensils, surfaces or pipework associated with the production, transport,
storage or consumption of food or feed (including drinking water) for
humans and animals
Group 1: 5: Drinking water Products used for the disinfection of drinking water for both humans and
Disinfectants animals
Group 3: Pest 18: Insecticides, acaricides and Products used for the control of arthropods (e.g., insects, arachnids and
control products to control other crustaceans), by means other than repulsion or attraction
arthropods
Group 3: Pest 19: Repellents and attractants Products used to control harmful organisms (invertebrates such as fleas,
control vertebrates such as birds, fish, rodents), by repelling or attracting,
including those that are used for human or veterinary hygiene either
directly on the skin or indirectly in the environment of human or animals
Group 4: Other 21: Antifouling products Products used to control the growth and settlement of fouling organisms
biocidal products (microbes and higher forms of plant or animal species) on vessels,
aquaculture equipment, or other structures used in water
marker residues, animal species in which the substance is human or veterinary medicine drugs when using antimi-
authorized, MRLs, target tissues, therapeutic classification crobials as growth promoters.
and other provisions according to Article 14(7) of In 1997, the European Commission introduced a
Regulation (EC) No. 470/2009 (EC, 2009a). In addition, requirement to monitor the occurrence of resistance in ani-
Commission Directive 2009/8/EC (EC, 2009a) sets maxi- mal bacteria associated with the use of antimicrobial feed
mum content levels for 11 coccidiostats in feed including additives and related substances (EC, 1997), suspending,
lasalocid sodium, narasin, salinomycin, monensin sodium, at the same time, the use of avoparcin as a feed additive in
semduramicin sodium, maduramicin ammonium, robeni- January 1997 and ardacin in January 1998. This obligation
dine hydrochloride, decoquinate, halofuginone hydrochlo- was reconfirmed by Council Regulation (EC) No. 2821/98
ride, nicarbazin, and diclazuril. These maximum levels (EC, 1998a) suspending in December 1998 the use of four
are set in mg/kg (ppm) relative to a feed stuff with a other antibiotics (zinc bacitracin, virginiamycin, tylosin
moisture content of 12%. phosphate, and spiramycin) that had been used as growth
Regulations have introduced many new aspects into promoters in feed under the conditions that their use
the preexisting legislation on feed additives, having been should be reexamined (Anado ´n and Martı ´nez-Larran ˜aga,
one of the first pieces of food safety legislation adopted 1999). Subsequently, the European Commission supported
following Regulation (EC) No. 178/2002 (EC, 2002b). By a surveillance program, conducted by industry, to monitor
introducing the granting of time-limited authorizations antimicrobial resistance against feed additives in bacteria
valid for a period of 10 years and by setting up a isolated from pigs and broiler chickens in the slaughter-
Community Reference Laboratory for feed additives, the houses in six European countries. However, as stated in
possibility of establishing MRLs for certain additives that the “White Paper on Food Additives” (adopted January
may result in residues when added to feed is greatly 2000), the European Commission at that time already con-
increased and the possibility of laying down postmarket- sidered the prohibition or phase-out of antibiotics used as
ing monitoring programs at the time of authorization is growth promoters within the EU, as part of a broader strat-
enhanced as well as other provisions. The regulation also egy to control and combat antibiotic resistance. With the
kept coccidiostats and introduced histomonostats as a new aim of avoiding economic losses, in particular in the pro-
category of feed additive, while establishing the phasing duction of pigs and broiler chickens, and to avoid a signif-
out of the use (and marketing) of the existing antibiotics icant increase in the use of antimicrobials under veterinary
as feed additives from January 1, 2006, taking into prescriptions, the EC supported the view that the phasing
account the risks of selecting bacterial strains resistant to out of antimicrobial feed additives would be easier to