Page 180 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 180
Toxicological Testing: In Vivo and In Vitro Models Chapter | 9 147
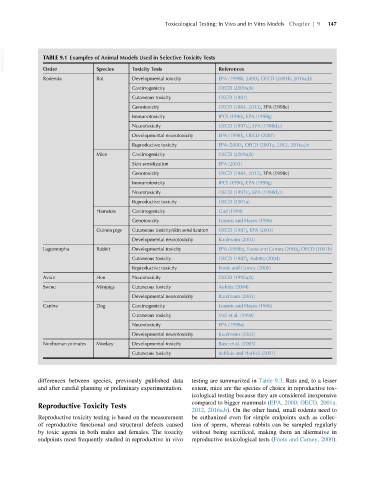
VetBooks.ir TABLE 9.1 Examples of Animal Models Used in Selective Toxicity Tests References
Species
Toxicity Tests
Order
Rodentia Rat Developmental toxicity EPA (1998b, 2000), OECD (2001b, 2016a,b)
Carcinogenicity OECD (2009a,b)
Cutaneous toxicity OECD (1987)
Genotoxicity OECD (1984, 2013), EPA (1998c)
Immunotoxicity IPCS (1996), EPA (1998g)
Neurotoxicity OECD (1997c), EPA (1998d,e)
Developmental neurotoxicity EPA (1998f), OECD (2007)
Reproductive toxicity EPA (2000), OECD (2001a, 2012, 2016a,b)
Mice Carcinogenicity OECD (2009a,b)
Skin sensitization EPA (2003)
Genotoxicity OECD (1984, 2013), EPA (1998c)
Immunotoxicity IPCS (1996), EPA (1998g)
Neurotoxicity OECD (1997c), EPA (1998d,e)
Reproductive toxicity OECD (2001a)
Hamsters Carcinogenicity Gad (1998)
Genotoxicity Loomis and Hayes (1996)
Guinea pigs Cutaneous toxicity/skin sensitization OECD (1987), EPA (2003)
Developmental neurotoxicity Kaufmann (2003)
Lagomorpha Rabbit Developmental toxicity EPA (1998b), Foote and Carney (2000), OECD (2001b)
Cutaneous toxicity OECD (1987), Auletta (2004)
Reproductive toxicity Foote and Carney (2000)
Avian Hen Neurotoxicity OECD (1995a,b)
Swine Minipigs Cutaneous toxicity Auletta (2004)
Developmental neurotoxicity Kaufmann (2003)
Canine Dog Carcinogenicity Loomis and Hayes (1996)
Cutaneous toxicity Vail et al. (1998)
Neurotoxicity EPA (1998e)
Developmental neurotoxicity Kaufmann (2003)
Nonhuman primates Monkey Developmental toxicity Buse et al. (2003)
Cutaneous toxicity deBlois and Horlick (2001)
differences between species, previously published data testing are summarized in Table 9.3. Rats and, to a lesser
and after careful planning or preliminary experimentation. extent, mice are the species of choice in reproductive tox-
icological testing because they are considered inexpensive
compared to bigger mammals (EPA, 2000; OECD, 2001a,
Reproductive Toxicity Tests
2012, 2016a,b). On the other hand, small rodents need to
Reproductive toxicity testing is based on the measurement be euthanized even for simple endpoints such as collec-
of reproductive functional and structural defects caused tion of sperm, whereas rabbits can be sampled regularly
by toxic agents in both males and females. The toxicity without being sacrificed, making them an alternative in
endpoints most frequently studied in reproductive in vivo reproductive toxicological tests (Foote and Carney, 2000).