Page 380 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 380
Carcinogenesis: Mechanisms and Models Chapter | 20 347
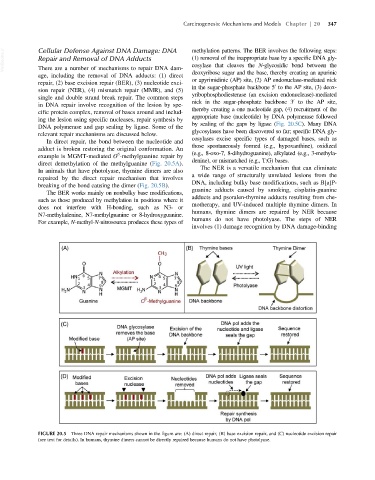
VetBooks.ir Cellular Defense Against DNA Damage: DNA methylation patterns. The BER involves the following steps:
(1) removal of the inappropriate base by a specific DNA gly-
Repair and Removal of DNA Adducts
cosylase that cleaves the N-glycosidic bond between the
There are a number of mechanisms to repair DNA dam-
age, including the removal of DNA adducts: (1) direct deoxyribose sugar and the base, thereby creating an apurinic
or apyrimidinic (AP) site, (2) AP endonuclase-mediated nick
repair, (2) base excision repair (BER), (3) nucleotide exci-
0
in the sugar-phosphate backbone 5 to the AP site, (3) deox-
sion repair (NER), (4) mismatch repair (MMR), and (5)
yribophosphodiesterase (an excision endonuclease)-mediated
single and double strand break repair. The common steps
nick in the sugar-phosphate backbone 3 to the AP site,
0
in DNA repair involve recognition of the lesion by spe-
thereby creating a one nucleotide gap, (4) recruitment of the
cific protein complex, removal of bases around and includ-
appropriate base (nucleotide) by DNA polymerase followed
ing the lesion using specific nucleases, repair synthesis by
by sealing of the gaps by ligase (Fig. 20.5C). Many DNA
DNA polymerase and gap sealing by ligase. Some of the
glycosylases have been discovered so far; specific DNA gly-
relevant repair mechanisms are discussed below.
cosylases excise specific types of damaged bases, such as
In direct repair, the bond between the nucleotide and
those spontaneously formed (e.g., hypoxanthine), oxidized
adduct is broken restoring the original conformation. An
6
example is MGMT-mediated O -methylguanine repair by (e.g., 8-oxo-7, 8-dihydroguanine), alkylated (e.g., 3-methyla-
denine), or mismatched (e.g., T:G) bases.
direct demethylation of the methylguanine (Fig. 20.5A).
The NER is a versatile mechanism that can eliminate
In animals that have photolyase, thymine dimers are also
a wide range of structurally unrelated lesions from the
repaired by the direct repair mechanism that involves
DNA, including bulky base modifications, such as B[a]P-
breaking of the bond causing the dimer (Fig. 20.5B).
guanine adducts caused by smoking, cisplatin-guanine
The BER works mainly on nonbulky base modifications,
adducts and psoralen-thymine adducts resulting from che-
such as those produced by methylation in positions where it
motherapy, and UV-induced multiple thymine dimers. In
does not interfere with H-bonding, such as N3- or
humans, thymine dimers are repaired by NER because
N7-methyladenine, N7-methylguanine or 8-hydroxyguanine.
humans do not have photolyase. The steps of NER
For example, N-methyl-N-nitrosourea produces these types of
involves (1) damage recognition by DNA damage-binding
FIGURE 20.5 Three DNA repair mechanisms shown in the figure are: (A) direct repair, (B) base excision repair, and (C) nucleotide excision repair
(see text for details). In humans, thymine dimers cannot be directly repaired because humans do not have photolyase.