Page 849 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 849
Chemical-Induced Estrogenicity Chapter | 59 807
VetBooks.ir contaminants, and kepone induced estrogenic poisoning MECHANISMS OF ESTROGEN-INDUCED
TRANSACTIVATION: ERα AND ERβ
in a group of exposed production workers. The com-
pounds illustrated in Fig. 59.4 exhibit relatively weak
binding to the ER and induce reporter gene expression DOMAIN STRUCTURE
in transactivation assays in cell culture systems and The estrogen receptor (ER) is a member of the nuclear
some of these compounds exhibit uterotrophic effects in receptor superfamily of transcription factors, which
female rodents. The important toxicological question exhibit modular structures and similar mechanisms of
concerning these chemical estrogens is whether they dif- action. For example, the transactivation function of ER is
fer only in potency that’s governed by their intrinsic mediated by two separate but not mutually exclusive
estrogenicity and bioavailability based on their metabo- transactivation domains namely, ligand-independent acti-
lism and pharmacokinetics. However, since the estro- vation function (AF) 1 (within the A/B) and ligand-
genic activity of these compounds is receptor dependent AF-2 (within the ligand binding domain, LBD)
dependent, it is also possible that the estrogenic activity (Tora et al., 1989)(Fig. 59.5). The A/B domain is the
of structurally diverse xenoestrogens is unique and not least conserved region between ERα and ERβ with only
strictly governed by intrinsic ER binding affinities and 30% similarity at the amino acid level. The activity of
pharmacodynamic factors. AF-1 in ERβ is negligible on estrogen-responsive element
(ERE) reporter constructs compared to the AF-1 of ERα
in several different cell lines (Cowley and Parker, 1999).
OH OH ERα and ERβ also exhibit distinctive responses to the
synthetic antiestrogens such as tamoxifen and raloxifene,
which act as partial ER agonists for ERα and as pure ER
antagonists for ERβ (Barkhem et al., 1998). The functional
C H CH 3 CCl 3 differences between the respective A/B regions of ERα
9 19
CH 3 H and ERβ may explain their differences in ligand-dependent
activation (Matthews and Gustafsson, 2003). The AF-1
HO HO HO
region of ERα interacts with different transcriptional regu-
Nonylphenol (NP) Bisphenol A HPTE
lators and coactivators that affect ligand-independent trans-
activation. The activity of AF-1 is also regulated through
H C CH 3 kinase-dependent phosphorylation and the individual path-
3
O ways involved vary with cell and promoter context. In
most cell lines, both AFs act synergistically to attain maxi-
HO C OR
mum transcriptional activity while in other cells only one
O CH 3 AF may be activated (Benecke et al., 2000).
4-Methylbenzylidene camphor Alkyl hydroxybenzoates The DNA binding domain (DBD) (region C) is highly
(parabens)
conserved between ERα and ERβ and exhibits 96% iden-
tity. This domain contains two zinc finger (CI and CII) as
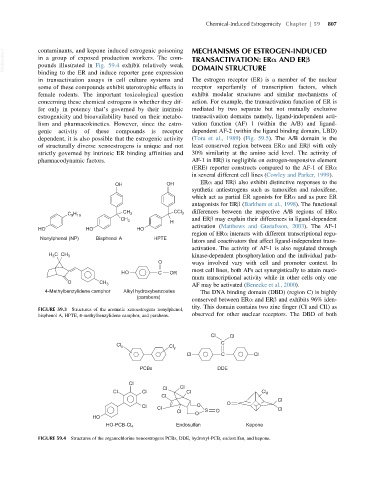
FIGURE 59.3 Structures of the aromatic xenoestrogens nonylphenol,
bisphenol A, HPTE, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor, and parabens. observed for other nuclear receptors. The DBD of both
Cl Cl
Cl x Cl y C
Cl C Cl
PCBs DDE
Cl
Cl Cl
Cl Cl Cl Cl 8
Cl
Cl
Cl O O
Cl Cl
Cl O S O
HO
HO-PCB-Cl 4 Endosulfan Kepone
FIGURE 59.4 Structures of the organochlorine xenoestrogens PCBs, DDE, hydroxyl-PCB, endosulfan, and kepone.