Page 851 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 851
Chemical-Induced Estrogenicity Chapter | 59 809
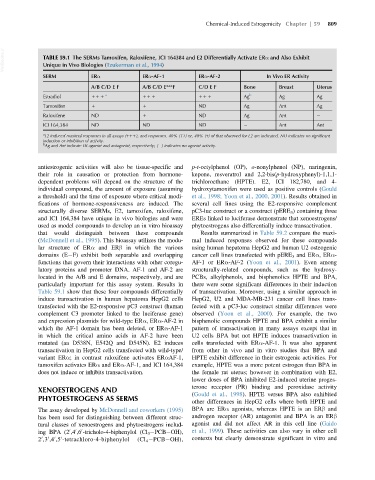
VetBooks.ir TABLE 59.1 The SERMs Tamoxifen, Raloxifene, ICI 164384 and E2 Differentially Activate ERα and Also Exhibit
Unique in Vivo Biologies (Tzukerman et al., 1994)
SERM ERα ERα-AF-1 ERα-AF-2 In Vivo ER Activity
A/B C/D E F A/B C/D E***F C/D E F Bone Breast Uterus
Estradiol 11 1 a 11 1 11 1 Ag b Ag Ag
Tamoxifen 1 1 ND Ag Ant Ag
Raloxifene ND 1 ND Ag Ant
ICI 164,384 ND ND ND Ant Ant
a
E2 induced maximal responses in all assays (111), and responses. 40% (11) or, 40% (1) of that observed for E2 are indicated. ND indicates no significant
induction or inhibition of activity.
b
Ag and Ant indicate ER agonist and antagonist, respectively; ( ) indicates no agonist activity.
antiestrogenic activities will also be tissue-specific and p-t-octylphenol (OP), o-nonylphenol (NP), naringenin,
their role in causation or protection from hormone- kepone, resveratrol and 2,2-bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)-1,1,1-
dependent problems will depend on the structure of the trichloroethane (HPTE). E2, ICI 182,780, and 4-
individual compound, the amount of exposure (assuming hydroxytamoxifen were used as positive controls (Gould
a threshold) and the time of exposure where critical modi- et al., 1998; Yoon et al., 2000, 2001). Results obtained in
fications of hormone-responsiveness are induced. The several cell lines using the E2-responsive complement
structurally diverse SERMs, E2, tamoxifen, raloxifene, pC3-luc construct or a construct (pERE 3 ) containing three
and ICI 164,384 have unique in vivo biologies and were EREs linked to luciferase demonstrate that xenoestrogens/
used as model compounds to develop an in vitro bioassay phytoestrogens also differentially induce transactivation.
that would distinguish between these compounds Results summarized in Table 59.2 compare the maxi-
(McDonnell et al., 1995). This bioassay utilizes the modu- mal induced responses observed for these compounds
lar structure of ERα and ERβ in which the various using human hepatoma HepG2 and human U2 osteogenic
domains (E F) exhibit both separable and overlapping cancer cell lines transfected with pERE 3 and ERα,ERα-
functions that govern their interactions with other coregu- AF-1 or ERα-AF-2 (Yoon et al., 2001). Even among
latory proteins and promoter DNA. AF-1 and AF-2 are structurally-related compounds, such as the hydroxy-
located in the A/B and E domains, respectively, and are PCBs, alkylphenols, and bisphenolics HPTE and BPA,
particularly important for this assay system. Results in there were some significant differences in their induction
Table 59.1 show that these four compounds differentially of transactivation. Moreover, using a similar approach in
induce transactivation in human hepatoma HepG2 cells HepG2, U2 and MDA-MB-231 cancer cell lines trans-
transfected with the E2-responsive pC3 construct (human fected with a pC3-luc construct similar differences were
complement C3 promoter linked to the luciferase gene) observed (Yoon et al., 2000). For example, the two
and expression plasmids for wild-type ERα,ERα-AF-2 in bisphenolic compounds HPTE and BPA exhibit a similar
which the AF-1 domain has been deleted, or ERα-AF-1 pattern of transactivation in many assays except that in
in which the critical amino acids in AF-2 have been U2 cells BPA but not HPTE induces transactivation in
mutated (aa D538N, E542Q and D545N). E2 induces cells transfected with ERα-AF-1. It was also apparent
transactivation in HepG2 cells transfected with wild-type/ from other in vivo and in vitro studies that BPA and
variant ERα; in contrast raloxifene activates ERαAF-1, HPTE exhibit difference in their estrogenic activities. For
tamoxifen activates ERα and ERα-AF-1, and ICI 164,384 example, HPTE was a more potent estrogen than BPA in
does not induce or inhibits transactivation. the female rat uterus; however in combination with E2,
lower doses of BPA inhibited E2-induced uterine proges-
terone receptor (PR) binding and peroxidase activity
XENOESTROGENS AND
(Gould et al., 1998). HPTE versus BPA also exhibited
PHYTOESTROGENS AS SERMS
other differences in HepG2 cells where both HPTE and
The assay developed by McDonnell and coworkers (1995) BPA are ERα agonists, whereas HPTE is an ERβ and
has been used for distinguishing between different struc- androgen receptor (AR) antagonist and BPA is an ERβ
tural classes of xenoestrogens and phytoestrogens includ- agonist and did not affect AR in this cell line (Gaido
0
0
ing BPA (2 ,4 ,6 -tricholo-4-biphenylol (Cl 3 PCB OH), et al., 1999). These activities can also vary in other cell
0
2 ,3 ,4 ,5 -tetrachloro-4-biphenylol (Cl 4 PCB OH), contexts but clearly demonstrate significant in vitro and
0
0
0
0