Page 853 - Veterinary Toxicology, Basic and Clinical Principles, 3rd Edition
P. 853
Chemical-Induced Estrogenicity Chapter | 59 811
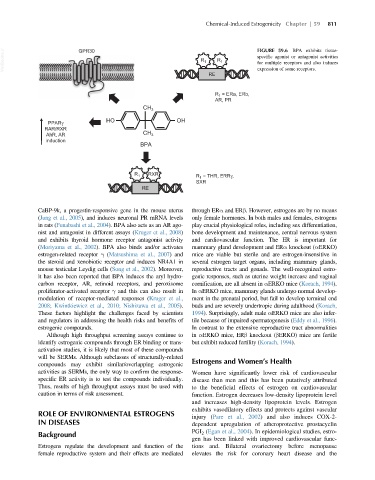
VetBooks.ir GPR30 R 1 R 1 FIGURE 59.6 BPA exhibits tissue-
specific agonist or antagonist activities
for multiple receptors and also induces
RE expression of some receptors.
R = ERa, ERb,
1
AR, PR
CH 3
PPARγ HO OH
RAR/RXR
AhR, AR CH 3
induction
BPA
R 1 RXR R = THR, ERRγ,
1
SXR
RE
CaBP-9k, a progestin-responsive gene in the mouse uterus through ERα and ERβ. However, estrogens are by no means
(Jung et al., 2005), and induces neuronal PR mRNA levels only female hormones. In both males and females, estrogens
in rats (Funabashi et al., 2004).BPAalsoactsasanARago- play crucial physiological roles, including sex differentiation,
nist and antagonist in different assays (Kruger et al., 2008) bone development and maintenance, central nervous system
and exhibits thyroid hormone receptor antagonist activity and cardiovascular function. The ER is important for
(Moriyama et al., 2002). BPA also binds and/or activates mammary gland development and ERα knockout (αERKO)
estrogen-related receptor γ (Matsushima et al., 2007)and mice are viable but sterile and are estrogen-insensitive in
the steroid and xenobiotic receptor and induces NR4A1 in several estrogen target organs, including mammary glands,
mouse testicular Leydig cells (Song et al., 2002). Moreover, reproductive tracts and gonads. The well-recognized estro-
it has also been reported that BPA induces the aryl hydro- genic responses, such as uterine weight increase and vaginal
carbon receptor, AR, retinoid receptors, and peroxisome cornification, are all absent in αERKO mice (Korach, 1994).
proliferator-activated receptor γ and this can also result in In αERKO mice, mammary glands undergo normal develop-
modulation of receptor-mediated responses (Kruger et al., ment in the prenatal period, but fail to develop terminal end
2008; Kwintkiewicz et al., 2010; Nishizawa et al., 2005). buds and are severely undertropic during adulthood (Korach,
These factors highlight the challenges faced by scientists 1994). Surprisingly, adult male αERKO mice are also infer-
and regulators in addressing the health risks and benefits of tile because of impaired spermatogenesis (Eddy et al., 1996).
estrogenic compounds. In contrast to the extensive reproductive tract abnormalities
Although high throughput screening assays continue to in αERKO mice, ERβ knockout (βERKO) mice are fertile
identify estrogenic compounds through ER binding or trans- but exhibit reduced fertility (Korach, 1994).
activation studies, it is likely that most of these compounds
will be SERMs. Although subclasses of structurally-related
Estrogens and Women’s Health
compounds may exhibit similar/overlapping estrogenic
activities as SERMs, the only way to confirm the response- Women have significantly lower risk of cardiovascular
specific ER activity is to test the compounds individually. disease than men and this has been putatively attributed
Thus, results of high throughput assays must be used with to the beneficial effects of estrogen on cardiovascular
caution in terms of risk assessment. function. Estrogen decreases low-density lipoprotein level
and increases high-density lipoprotein levels. Estrogen
exhibits vasodilatory effects and protects against vascular
ROLE OF ENVIRONMENTAL ESTROGENS
injury (Pare et al., 2002) and also induces COX-2-
IN DISEASES dependent upregulation of atheroprotective prostacyclin
PGI 2 (Egan et al., 2004). In epidemiological studies, estro-
Background
gen has been linked with improved cardiovascular func-
Estrogens regulate the development and function of the tions and. Bilateral ovariectomy before menopause
female reproductive system and their effects are mediated elevates the risk for coronary heart disease and the