Page 1231 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1231
CHAPTER 69 Disorders of the Joints 1203
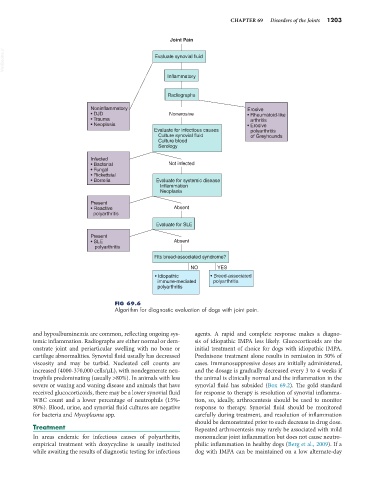
Joint Pain
VetBooks.ir Evaluate synovial fluid
Inflammatory
Radiographs
Noninflammatory Erosive
• DJD Nonerosive • Rheumatoid-like
• Trauma arthritis
• Neoplasia • Erosive
Evaluate for infectious causes polyarthritis
Culture synovial fluid of Greyhounds
Culture blood
Serology
Infected
• Bacterial Not infected
• Fungal
• Rickettsial
• Borrelia Evaluate for systemic disease
Inflammation
Neoplasia
Present
• Reactive Absent
polyarthritis
Evaluate for SLE
Present
• SLE Absent
polyarthritis
Fits breed-associated syndrome?
NO YES
• Idiopathic • Breed-associated
immune-mediated polyarthritis
polyarthritis
FIG 69.6
Algorithm for diagnostic evaluation of dogs with joint pain.
and hypoalbuminemia are common, reflecting ongoing sys- agents. A rapid and complete response makes a diagno-
temic inflammation. Radiographs are either normal or dem- sis of idiopathic IMPA less likely. Glucocorticoids are the
onstrate joint and periarticular swelling with no bone or initial treatment of choice for dogs with idiopathic IMPA.
cartilage abnormalities. Synovial fluid usually has decreased Prednisone treatment alone results in remission in 50% of
viscosity and may be turbid. Nucleated cell counts are cases. Immunosuppressive doses are initially administered,
increased (4000-370,000 cells/µL), with nondegenerate neu- and the dosage is gradually decreased every 3 to 4 weeks if
trophils predominating (usually >80%). In animals with less the animal is clinically normal and the inflammation in the
severe or waxing and waning disease and animals that have synovial fluid has subsided (Box 69.2). The gold standard
received glucocorticoids, there may be a lower synovial fluid for response to therapy is resolution of synovial inflamma-
WBC count and a lower percentage of neutrophils (15%- tion, so, ideally, arthrocentesis should be used to monitor
80%). Blood, urine, and synovial fluid cultures are negative response to therapy. Synovial fluid should be monitored
for bacteria and Mycoplasma spp. carefully during treatment, and resolution of inflammation
should be demonstrated prior to each decrease in drug dose.
Treatment Repeated arthrocentesis may rarely be associated with mild
In areas endemic for infectious causes of polyarthritis, mononuclear joint inflammation but does not cause neutro-
empirical treatment with doxycycline is usually instituted philic inflammation in healthy dogs (Berg et al., 2009). If a
while awaiting the results of diagnostic testing for infectious dog with IMPA can be maintained on a low alternate-day