Page 1291 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1291
CHAPTER 74 Cytology 1263
74.12). Because inflammation is an important component obtained in approximately 90% of dogs and 60% to 70%
of HCTs, inflammatory cells (i.e., neutrophils, lymphocytes) of cats with lymphadenopathy. If the cytologic findings of
VetBooks.ir are commonly found in these tumors. MCTs are distinctive an enlarged lymph node are inconclusive, the node should
be surgically excised and submitted for histopathologic
in that the cytoplasm of the neoplastic cells contains purple
(metachromatic) granules, which can be so numerous as to
When evaluating cytologic specimens prepared from
obscure the nuclear features; eosinophils are also a common evaluation.
feature in these tumors. Mast cell granules may be absent in lymph node aspirates or impression smears, the clinician
poorly differentiated tumors or in tumors stained with Diff- should keep in mind that these organs react to a variety of
Quik (Fig. 74.13). stimuli following a distinct pattern. In general, four cyto-
logic patterns are recognized: normal lymph node, reac-
LYMPH NODES tive or hyperplastic lymphadenopathy, lymphadenitis, and
Cytologic evaluation of lymph node aspirates is commonly neoplasia.
done in practice. In our clinics, a cytologic diagnosis is
Normal Lymph Node
Cytologic specimens from normal nodes are composed pre-
dominantly (≈70% to 90%) of small lymphocytes; thus they
are monomorphic. These cells are approximately 7 to 10 µm
in diameter (1-1.5 times the diameter of a red blood cell and
smaller than a neutrophil) and have a dense chromatin
pattern and no nucleoli. The remaining cells are macro-
phages, lymphoblasts, plasma cells, and other immune cells.
Reactive or Hyperplastic
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphoid tissues reacting to different antigenic stimuli (e.g.,
bacterial, fungal, neoplastic) are cytologically similar in that
the cell population is composed of a mixture of small, inter-
mediate, and large lymphocytes; lymphoblasts; plasma cells;
and macrophages (Fig. 74.14). In addition, other cell types
may be present, depending on the specific agent (e.g., eosin-
FIG 74.12 ophils in parasitic or allergic reactions). The first impression
Photomicrograph of a fine-needle aspirate from a small,
round, dermoepidermal mass in the head of a 1-year-old when evaluating a reactive or hyperplastic node cytologically
dog. Note the large round cells with abundant clear is that of a heterogeneous population of cells. The presence
cytoplasm and fine chromatin pattern. The diagnosis was of cells in different stages of development indicates that the
histiocytoma (×1000). lymphoid tissue is undergoing polyclonal expansion (i.e.,
A B
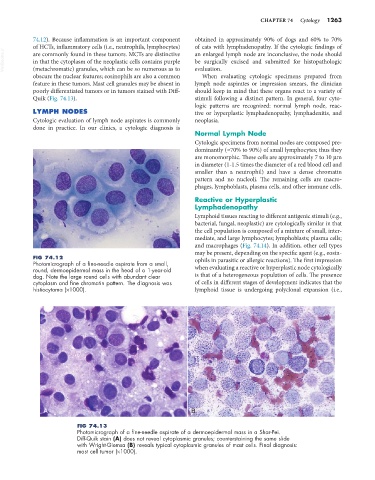
FIG 74.13
Photomicrograph of a fine-needle aspirate of a dermoepidermal mass in a Shar-Pei.
Diff-Quik stain (A) does not reveal cytoplasmic granules; counterstaining the same slide
with Wright-Giemsa (B) reveals typical cytoplasmic granules of mast cells. Final diagnosis:
mast cell tumor (×1000).