Page 672 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 672
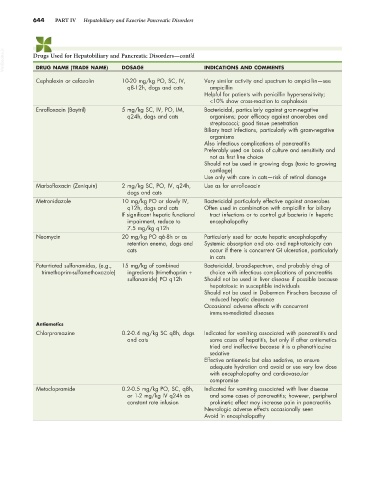
644 PART IV Hepatobiliary and Exocrine Pancreatic Disorders
VetBooks.ir Drugs Used for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disorders—cont’d INDICATIONS AND COMMENTS
DOSAGE
DRUG NAME (TRADE NAME)
Cephalexin or cefazolin 10-20 mg/kg PO, SC, IV, Very similar activity and spectrum to ampicillin—see
q8-12h, dogs and cats ampicillin
Helpful for patients with penicillin hypersensitivity;
<10% show cross-reaction to cephalexin
Enrofloxacin (Baytril) 5 mg/kg SC, IV, PO, IM, Bactericidal, particularly against gram-negative
q24h, dogs and cats organisms; poor efficacy against anaerobes and
streptococci; good tissue penetration
Biliary tract infections, particularly with gram-negative
organisms
Also infectious complications of pancreatitis
Preferably used on basis of culture and sensitivity and
not as first line choice
Should not be used in growing dogs (toxic to growing
cartilage)
Use only with care in cats—risk of retinal damage
Marbofloxacin (Zeniquin) 2 mg/kg SC, PO, IV, q24h, Use as for enrofloxacin
dogs and cats
Metronidazole 10 mg/kg PO or slowly IV, Bactericidal particularly effective against anaerobes
q12h, dogs and cats Often used in combination with ampicillin for biliary
If significant hepatic functional tract infections or to control gut bacteria in hepatic
impairment, reduce to encephalopathy
7.5 mg/kg q12h
Neomycin 20 mg/kg PO q6-8h or as Particularly used for acute hepatic encephalopathy
retention enema, dogs and Systemic absorption and oto- and nephrotoxicity can
cats occur if there is concurrent GI ulceration, particularly
in cats
Potentiated sulfonamides, (e.g., 15 mg/kg of combined Bactericidal, broad-spectrum, and probably drug of
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) ingredients (trimethoprim + choice with infectious complications of pancreatitis
sulfonamide) PO q12h Should not be used in liver disease if possible because
hepatotoxic in susceptible individuals
Should not be used in Doberman Pinschers because of
reduced hepatic clearance
Occasional adverse effects with concurrent
immune-mediated diseases
Antiemetics
Chlorpromazine 0.2-0.4 mg/kg SC q8h, dogs Indicated for vomiting associated with pancreatitis and
and cats some cases of hepatitis, but only if other antiemetics
tried and ineffective because it is a phenothiazine
sedative
Effective antiemetic but also sedative, so ensure
adequate hydration and avoid or use very low dose
with encephalopathy and cardiovascular
compromise
Metoclopramide 0.2-0.5 mg/kg PO, SC, q8h, Indicated for vomiting associated with liver disease
or 1-2 mg/kg IV q24h as and some cases of pancreatitis; however, peripheral
constant rate infusion prokinetic effect may increase pain in pancreatitis
Neurologic adverse effects occasionally seen
Avoid in encephalopathy