Page 675 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 675
CHAPTER 37 The Exocrine Pancreas 647
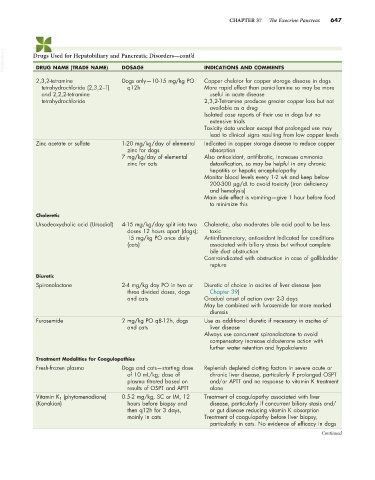
VetBooks.ir Drugs Used for Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Disorders—cont’d INDICATIONS AND COMMENTS
DOSAGE
DRUG NAME (TRADE NAME)
2,3,2-tetramine Dogs only—10-15 mg/kg PO Copper chelator for copper storage disease in dogs
tetrahydrochloride (2,3,2−T) q12h More rapid effect than penicillamine so may be more
and 2,2,2-tetramine useful in acute disease
tetrahydrochloride 2,3,2-Tetramine produces greater copper loss but not
available as a drug
Isolated case reports of their use in dogs but no
extensive trials
Toxicity data unclear except that prolonged use may
lead to clinical signs resulting from low copper levels
Zinc acetate or sulfate 1-20 mg/kg/day of elemental Indicated in copper storage disease to reduce copper
zinc for dogs absorption
7 mg/kg/day of elemental Also antioxidant, antifibrotic, increases ammonia
zinc for cats detoxification, so may be helpful in any chronic
hepatitis or hepatic encephalopathy
Monitor blood levels every 1-2 wk and keep below
200-300 µg/dL to avoid toxicity (iron deficiency
and hemolysis)
Main side effect is vomiting—give 1 hour before food
to minimize this
Choleretic
Ursodeoxycholic acid (Ursodiol) 4-15 mg/kg/day split into two Choleretic, also moderates bile acid pool to be less
doses 12 hours apart (dogs); toxic
15 mg/kg PO once daily Antiinflammatory, antioxidant Indicated for conditions
(cats) associated with biliary stasis but without complete
bile duct obstruction
Contraindicated with obstruction in case of gallbladder
rupture
Diuretic
Spironolactone 2-4 mg/kg day PO in two or Diuretic of choice in ascites of liver disease (see
three divided doses, dogs Chapter 39)
and cats Gradual onset of action over 2-3 days
May be combined with furosemide for more marked
diuresis
Furosemide 2 mg/kg PO q8-12h, dogs Use as additional diuretic if necessary in ascites of
and cats liver disease
Always use concurrent spironolactone to avoid
compensatory increase aldosterone action with
further water retention and hypokalemia
Treatment Modalities for Coagulopathies
Fresh-frozen plasma Dogs and cats—starting dose Replenish depleted clotting factors in severe acute or
of 10 mL/kg; dose of chronic liver disease, particularly if prolonged OSPT
plasma titrated based on and/or APTT and no response to vitamin K treatment
results of OSPT and APTT alone
Vitamin K 1 (phytomenadione) 0.5-2 mg/kg, SC or IM, 12 Treatment of coagulopathy associated with liver
(Konakion) hours before biopsy and disease, particularly if concurrent biliary stasis and/
then q12h for 3 days, or gut disease reducing vitamin K absorption
mainly in cats Treatment of coagulopathy before liver biopsy,
particularly in cats. No evidence of efficacy in dogs
Continued