Page 682 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 682
654 PART V Urinary Tract Disorders
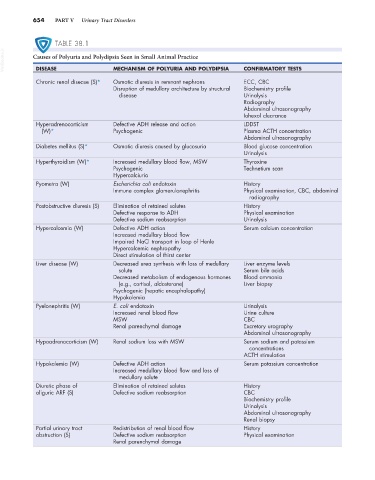
TABLE 38.1
VetBooks.ir Causes of Polyuria and Polydipsia Seen in Small Animal Practice CONFIRMATORY TESTS
MECHANISM OF POLYURIA AND POLYDIPSIA
DISEASE
Chronic renal disease (S)* Osmotic diuresis in remnant nephrons ECC, CBC
Disruption of medullary architecture by structural Biochemistry profile
disease Urinalysis
Radiography
Abdominal ultrasonography
Iohexol clearance
Hyperadrenocorticism Defective ADH release and action LDDST
(W)* Psychogenic Plasma ACTH concentration
Abdominal ultrasonography
Diabetes mellitus (S)* Osmotic diuresis caused by glucosuria Blood glucose concentration
Urinalysis
Hyperthyroidism (W)* Increased medullary blood flow, MSW Thyroxine
Psychogenic Technetium scan
Hypercalciuria
Pyometra (W) Escherichia coli endotoxin History
Immune complex glomerulonephritis Physical examination, CBC, abdominal
radiography
Postobstructive diuresis (S) Elimination of retained solutes History
Defective response to ADH Physical examination
Defective sodium reabsorption Urinalysis
Hypercalcemia (W) Defective ADH action Serum calcium concentration
Increased medullary blood flow
Impaired NaCl transport in loop of Henle
Hypercalcemic nephropathy
Direct stimulation of thirst center
Liver disease (W) Decreased urea synthesis with loss of medullary Liver enzyme levels
solute Serum bile acids
Decreased metabolism of endogenous hormones Blood ammonia
(e.g., cortisol, aldosterone) Liver biopsy
Psychogenic (hepatic encephalopathy)
Hypokalemia
Pyelonephritis (W) E. coli endotoxin Urinalysis
Increased renal blood flow Urine culture
MSW CBC
Renal parenchymal damage Excretory urography
Abdominal ultrasonography
Hypoadrenocorticism (W) Renal sodium loss with MSW Serum sodium and potassium
concentrations
ACTH stimulation
Hypokalemia (W) Defective ADH action Serum potassium concentration
Increased medullary blood flow and loss of
medullary solute
Diuretic phase of Elimination of retained solutes History
oliguric ARF (S) Defective sodium reabsorption CBC
Biochemistry profile
Urinalysis
Abdominal ultrasonography
Renal biopsy
Partial urinary tract Redistribution of renal blood flow History
obstruction (S) Defective sodium reabsorption Physical examination
Renal parenchymal damage