Page 696 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 696
668 PART V Urinary Tract Disorders
VetBooks.ir
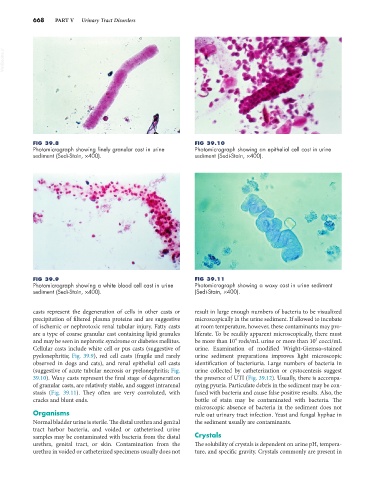
FIG 39.8 FIG 39.10
Photomicrograph showing finely granular cast in urine Photomicrograph showing an epithelial cell cast in urine
sediment (Sedi-Stain, ×400). sediment (Sedi-Stain, ×400).
FIG 39.9 FIG 39.11
Photomicrograph showing a white blood cell cast in urine Photomicrograph showing a waxy cast in urine sediment
sediment (Sedi-Stain, ×400). (Sedi-Stain, ×400).
casts represent the degeneration of cells in other casts or result in large enough numbers of bacteria to be visualized
precipitation of filtered plasma proteins and are suggestive microscopically in the urine sediment. If allowed to incubate
of ischemic or nephrotoxic renal tubular injury. Fatty casts at room temperature, however, these contaminants may pro-
are a type of coarse granular cast containing lipid granules liferate. To be readily apparent microscopically, there must
5
4
and may be seen in nephrotic syndrome or diabetes mellitus. be more than 10 rods/mL urine or more than 10 cocci/mL
Cellular casts include white cell or pus casts (suggestive of urine. Examination of modified Wright-Giemsa–stained
pyelonephritis; Fig. 39.9), red cell casts (fragile and rarely urine sediment preparations improves light microscopic
observed in dogs and cats), and renal epithelial cell casts identification of bacteriuria. Large numbers of bacteria in
(suggestive of acute tubular necrosis or pyelonephritis; Fig. urine collected by catheterization or cystocentesis suggest
39.10). Waxy casts represent the final stage of degeneration the presence of UTI (Fig. 39.12). Usually, there is accompa-
of granular casts, are relatively stable, and suggest intrarenal nying pyuria. Particulate debris in the sediment may be con-
stasis (Fig. 39.11). They often are very convoluted, with fused with bacteria and cause false positive results. Also, the
cracks and blunt ends. bottle of stain may be contaminated with bacteria. The
microscopic absence of bacteria in the sediment does not
Organisms rule out urinary tract infection. Yeast and fungal hyphae in
Normal bladder urine is sterile. The distal urethra and genital the sediment usually are contaminants.
tract harbor bacteria, and voided or catheterized urine
samples may be contaminated with bacteria from the distal Crystals
urethra, genital tract, or skin. Contamination from the The solubility of crystals is dependent on urine pH, tempera-
urethra in voided or catheterized specimens usually does not ture, and specific gravity. Crystals commonly are present in