Page 773 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 773
CHAPTER 46 Disorders of the Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland 745
1.035
BOX 46.2
VetBooks.ir 1.030 Therapies Available for Polydipsic/Polyuric Dogs and
Cats With Central Diabetes Insipidus, Nephrogenic
Diabetes Insipidus, or Primary (Psychogenic) Polydipsia
A. Central diabetes insipidus (severe)
1.025 1. DDAVP (desmopressin acetate)
a. Effective
b. Expensive
c. Oral tablets or drops of nasal solution in
Urine specific gravity 1.015 2. LVP (lypressin [Diapid])
1.020
conjunctival sac
a. Short duration of action; less potent than
DDAVP
b. Expensive
c. Requires drops into nose or conjunctival sac
3. No treatment—provide continuous source of water
B. Central diabetes insipidus (partial)
1.010
1. DDAVP
2. LVP
3. Chlorpropamide
a. 30%-70% effective
1.005
b. Inexpensive
c. Pill form
d. Takes 1-2 weeks for effect of drug to be noted
e. May cause hypoglycemia
0 4. Thiazide diuretics
Hydrated 5% Post-AVP
Dehydration administration a. Mildly effective
b. Inexpensive
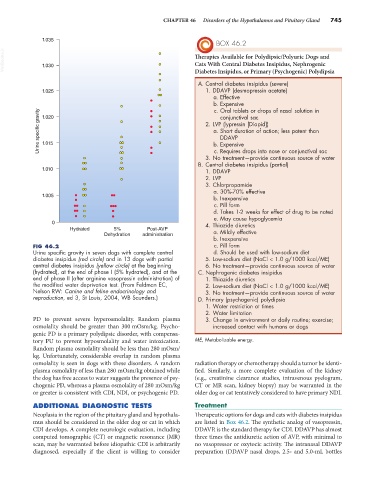
FIG 46.2 c. Pill form
Urine specific gravity in seven dogs with complete central d. Should be used with low-sodium diet
diabetes insipidus (red circle) and in 13 dogs with partial 5. Low-sodium diet (NaCl < 1.0 g/1000 kcal/ME)
central diabetes insipidus (yellow circle) at the beginning 6. No treatment—provide continuous source of water
(hydrated), at the end of phase I (5% hydrated), and at the C. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
end of phase II (after arginine vasopressin administration) of 1. Thiazide diuretics
the modified water deprivation test. (From Feldman EC, 2. Low-sodium diet (NaCl < 1.0 g/1000 kcal/ME)
Nelson RW: Canine and feline endocrinology and 3. No treatment—provide continuous source of water
reproduction, ed 3, St Louis, 2004, WB Saunders.) D. Primary (psychogenic) polydipsia
1. Water restriction at times
2. Water limitation
PD to prevent severe hyperosmolality. Random plasma 3. Change in environment or daily routine; exercise;
osmolality should be greater than 300 mOsm/kg. Psycho- increased contact with humans or dogs
genic PD is a primary polydipsic disorder, with compensa-
tory PU to prevent hyposmolality and water intoxication. ME, Metabolizable energy.
Random plasma osmolality should be less than 280 mOsm/
kg. Unfortunately, considerable overlap in random plasma
osmolality is seen in dogs with these disorders. A random radiation therapy or chemotherapy should a tumor be identi-
plasma osmolality of less than 280 mOsm/kg obtained while fied. Similarly, a more complete evaluation of the kidney
the dog has free access to water suggests the presence of psy- (e.g., creatinine clearance studies, intravenous pyelogram,
chogenic PD, whereas a plasma osmolality of 280 mOsm/kg CT or MR scan, kidney biopsy) may be warranted in the
or greater is consistent with CDI, NDI, or psychogenic PD. older dog or cat tentatively considered to have primary NDI.
ADDITIONAL DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Treatment
Neoplasia in the region of the pituitary gland and hypothala- Therapeutic options for dogs and cats with diabetes insipidus
mus should be considered in the older dog or cat in which are listed in Box 46.2. The synthetic analog of vasopressin,
CDI develops. A complete neurologic evaluation, including DDAVP, is the standard therapy for CDI. DDAVP has almost
computed tomographic (CT) or magnetic resonance (MR) three times the antidiuretic action of AVP, with minimal to
scan, may be warranted before idiopathic CDI is arbitrarily no vasopressor or oxytocic activity. The intranasal DDAVP
diagnosed, especially if the client is willing to consider preparation (DDAVP nasal drops, 2.5- and 5.0-mL bottles