Page 778 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 778
750 PART VI Endocrine Disorders
VetBooks.ir
B
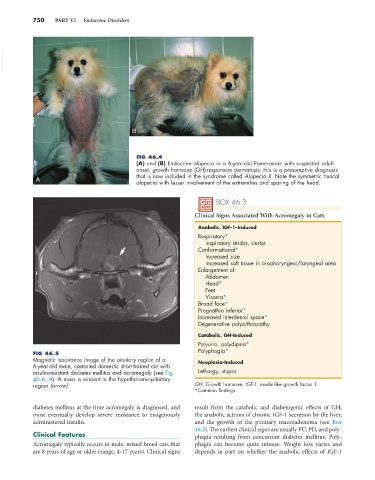
FIG 46.4
(A) and (B) Endocrine alopecia in a 6-year-old Pomeranian with suspected adult-
onset, growth hormone (GH)-responsive dermatosis; this is a presumptive diagnosis
that is now included in the syndrome called Alopecia X. Note the symmetric truncal
A
alopecia with lesser involvement of the extremities and sparing of the head.
BOX 46.3
Clinical Signs Associated With Acromegaly in Cats
Anabolic, IGF-1–Induced
Respiratory*
Inspiratory stridor, stertor
Conformational*
Increased size
Increased soft tissue in oropharyngeal/laryngeal area
Enlargement of:
Abdomen
Head*
Feet
Viscera*
Broad face*
Prognathia inferior*
Increased interdental space*
Degenerative polyarthropathy
Catabolic, GH-Induced
Polyuria, polydipsia*
FIG 46.5 Polyphagia*
Magnetic resonance image of the pituitary region of a Neoplasia-Induced
6-year-old male, castrated domestic short-haired cat with
insulin-resistant diabetes mellitus and acromegaly (see Fig. Lethargy, stupor
46.6, A). A mass is evident in the hypothalamic-pituitary
region (arrow). GH, Growth hormone; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1.
*Common findings.
diabetes mellitus at the time acromegaly is diagnosed, and result from the catabolic and diabetogenic effects of GH,
most eventually develop severe resistance to exogenously the anabolic actions of chronic IGF-1 secretion by the liver,
administered insulin. and the growth of the pituitary macroadenoma (see Box
46.3). The earliest clinical signs are usually PU, PD, and poly-
Clinical Features phagia resulting from concurrent diabetes mellitus. Poly-
Acromegaly typically occurs in male, mixed-breed cats that phagia can become quite intense. Weight loss varies and
are 8 years of age or older (range, 4-17 years). Clinical signs depends in part on whether the anabolic effects of IGF-1