Page 790 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 790
762 PART VI Endocrine Disorders
and cats with PHP have a solitary, easily identified parathy-
roid adenoma (see Fig. 47.1). Enlargement of more than one
VetBooks.ir parathyroid gland indicates the presence of multiple adeno-
mas or parathyroid hyperplasia. If none of the parathyroid
glands appears enlarged, or if all appear small, the diagnosis
of PHP must be questioned, and hypercalcemia stemming
from occult neoplasia or PTH production by a parathyroid
tumor in an ectopic site (often located in the soft tissues near
the thyroid gland) or by a nonparathyroid tumor should be
considered.
Chemical (i.e., ethanol) or radiofrequency heat ablation
of abnormal parathyroid tissue performed under ultrasound
guidance is effective treatment for PHP (Fig. 47.4). Surgery
is avoided, anesthetic time is significantly reduced, and no
FIG 47.2
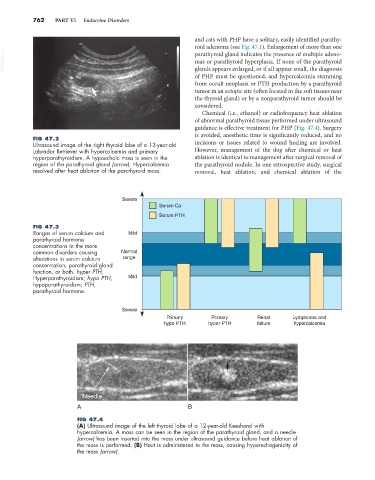
Ultrasound image of the right thyroid lobe of a 13-year-old incisions or issues related to wound healing are involved.
Labrador Retriever with hypercalcemia and primary However, management of the dog after chemical or heat
hyperparathyroidism. A hypoechoic mass is seen in the ablation is identical to management after surgical removal of
region of the parathyroid gland (arrow). Hypercalcemia the parathyroid nodule. In one retrospective study, surgical
resolved after heat ablation of the parathyroid mass. removal, heat ablation, and chemical ablation of the
Severe
Serum Ca
Serum PTH
FIG 47.3
Ranges of serum calcium and Mild
parathyroid hormone
concentrations in the more
common disorders causing Normal
alterations in serum calcium range
concentration, parathyroid gland
function, or both. hyper PTH,
Hyperparathyroidism; hypo PTH, Mild
hypoparathyroidism; PTH,
parathyroid hormone.
Severe
Primary Primary Renal Lymphoma and
hypo PTH hyper PTH failure hypercalcemia
A B
FIG 47.4
(A) Ultrasound image of the left thyroid lobe of a 12-year-old Keeshond with
hypercalcemia. A mass can be seen in the region of the parathyroid gland, and a needle
(arrow) has been inserted into the mass under ultrasound guidance before heat ablation of
the mass is performed. (B) Heat is administered to the mass, causing hyperechogenicity of
the mass (arrow).