Page 827 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 827
CHAPTER 48 Disorders of the Thyroid Gland 799
to 4 months. The goal is to maintain the serum calcium 500
concentration between 8 and 10 mg/dL. If hypocalcemia
VetBooks.ir recurs, therapy with vitamin D and calcium should be 400
reinstituted.
Hypothyroidism may develop in some cats after bilateral
thyroidectomy. The clinical signs, diagnosis, and treatment 300
are discussed on page 790. The decision to initiate levothy-
roxine treatment should be based on the presence or absence 250
of clinical signs and changes in the serum creatinine
concentration—not on the serum T 4 concentration, per se.
Serum T 4 concentrations commonly decrease after surgery, Serum thyroxine (nmol/L) 200
often to less than 0.5 µg/dL (6 nmol/L), but thyroid function
returns in most cats before clinical signs become apparent.
Thyroid hormone supplementation should be initiated in 150
cats that develop clinical signs in conjunction with a low
serum T 4 concentration and in cats that develop azotemia as 100
a result of decreased GFR induced by the low serum T 4 con-
centration. Because thyroid hormone replacement therapy
may not be needed long term in some of these cats, it should 50
be tapered slowly and then discontinued after 2 to 3 months
while monitoring serum T 4 and creatinine concentrations so 0
the continued need for treatment can be determined. Pretreatment 7-25 days 2-3 months 6-12 months
If clinical signs of hyperthyroidism persist despite thy- (524) (524) (519) (502)
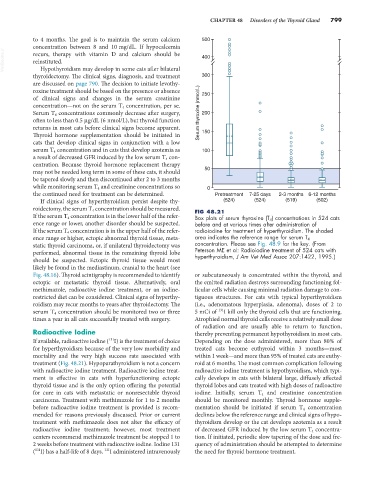
roidectomy, the serum T 4 concentration should be measured. FIG 48.21
If the serum T 4 concentration is in the lower half of the refer- Box plots of serum thyroxine (T 4 ) concentrations in 524 cats
ence range or lower, another disorder should be suspected. before and at various times after administration of
If the serum T 4 concentration is in the upper half of the refer- radioiodine for treatment of hyperthyroidism. The shaded
ence range or higher, ectopic abnormal thyroid tissue, meta- area indicates the reference range for serum T 4
static thyroid carcinoma, or, if unilateral thyroidectomy was concentration. Please see Fig. 48.9 for the key. (From
performed, abnormal tissue in the remaining thyroid lobe Peterson ME et al: Radioiodine treatment of 524 cats with
hyperthyroidism, J Am Vet Med Assoc 207:1422, 1995.)
should be suspected. Ectopic thyroid tissue would most
likely be found in the mediastinum, cranial to the heart (see
Fig. 48.16). Thyroid scintigraphy is recommended to identify or subcutaneously is concentrated within the thyroid, and
ectopic or metastatic thyroid tissue. Alternatively, oral the emitted radiation destroys surrounding functioning fol-
methimazole, radioactive iodine treatment, or an iodine- licular cells while causing minimal radiation damage to con-
restricted diet can be considered. Clinical signs of hyperthy- tiguous structures. For cats with typical hyperthyroidism
roidism may recur months to years after thyroidectomy. The (i.e., adenomatous hyperplasia, adenoma), doses of 2 to
131
serum T 4 concentration should be monitored two or three 5 mCi of I kill only the thyroid cells that are functioning.
times a year in all cats successfully treated with surgery. Atrophied normal thyroid cells receive a relatively small dose
of radiation and are usually able to return to function,
Radioactive Iodine thereby preventing permanent hypothyroidism in most cats.
131
If available, radioactive iodine ( I) is the treatment of choice Depending on the dose administered, more than 80% of
for hyperthyroidism because of the very low morbidity and treated cats become euthyroid within 3 months—most
mortality and the very high success rate associated with within 1 week—and more than 95% of treated cats are euthy-
treatment (Fig. 48.21). Hypoparathyroidism is not a concern roid at 6 months. The most common complication following
with radioactive iodine treatment. Radioactive iodine treat- radioactive iodine treatment is hypothyroidism, which typi-
ment is effective in cats with hyperfunctioning ectopic cally develops in cats with bilateral large, diffusely affected
thyroid tissue and is the only option offering the potential thyroid lobes and cats treated with high doses of radioactive
for cure in cats with metastatic or nonresectable thyroid iodine. Initially, serum T 4 and creatinine concentration
carcinoma. Treatment with methimazole for 1 to 2 months should be monitored monthly. Thyroid hormone supple-
before radioactive iodine treatment is provided is recom- mentation should be initiated if serum T 4 concentration
mended for reasons previously discussed. Prior or current declines below the reference range and clinical signs of hypo-
treatment with methimazole does not alter the efficacy of thyroidism develop or the cat develops azotemia as a result
radioactive iodine treatment; however, most treatment of decreased GFR induced by the low serum T 4 concentra-
centers recommend methimazole treatment be stopped 1 to tion. If initiated, periodic slow tapering of the dose and fre-
2 weeks before treatment with radioactive iodine. Iodine 131 quency of administration should be attempted to determine
( I) has a half-life of 8 days. I administered intravenously the need for thyroid hormone treatment.
131
131