Page 151 - Withrow and MacEwen's Small Animal Clinical Oncology, 6th Edition
P. 151
130 PART II Diagnostic Procedures for the Cancer Patient
should not be confused with apoptotic or pyknotic cells, which Description of Neoplastic Populations
retain distinct cytoplasmic borders that surround condensed Determination of the number of cells exfoliated and the shape
nuclear fragments.
VetBooks.ir rhage leading to the presence of few or many erythrocytes admixed and arrangement of cells early in the cytologic evaluation aids
Aspiration usually results in some degree of sampling hemor-
in formulating an initial list of differential diagnoses, permit-
with nucleated cells. Aspiration of splenic lesions and thyroid and ting placement of tumors in three broad categories: epithelial,
vascular tumors may result in pronounced hemorrhage and abun- mesenchymal, and discrete round cell tumors. Briefly, cells from
dant blood in the cytologic specimen. Preexisting intralesional epithelial tumors exfoliate well and are round, cuboidal, colum-
hemorrhage is indicated by the presence of macrophages contain- nar, or polygonal cells arranged in cohesive sheets or clusters;
ing erythrocytes or hemosiderin. Small numbers of peripheral cells from mesenchymal tumors exfoliate poorly and are spindle,
leukocytes, primarily neutrophils, will accompany hemorrhage, stellate, or oval cells arranged individually or in noncohesive
but the presence of neutrophils in numbers greater than their aggregates; and cells from discrete round cell tumors exfoliate
proportion in blood is supportive of inflammation. Neutrophilic well and are individualized round cells that are arranged in a
inflammation may accompany tumors, most notably squamous monolayer. Cellular arrangements observed in cytologic speci-
cell carcinoma and large tumors with necrotic centers; however, mens and their associated histologic correlates and tissue types
inflammation can induce criteria of malignancy in nonneoplastic have been described. 5
populations, especially fibroblasts and squamous cells, and surgi- Proper terminology should be used to succinctly describe cell
cal biopsy may be required to confirm suspected neoplasia when populations and convey important information. The terms homo-
inflammation is prominent. Some tumors are associated with infil- geneous and heterogeneous describe cell populations (Figs. 7.4 and
tration of specific inflammatory cells (e.g., eosinophils in MCTs). 7.5). Homogeneous denotes a population of one cell type (exclud-
For tumors that produce ground substance(s), such as sarco- ing erythrocytes and associated leukocytes), which is typical of
mas, or that elicit a scirrhous response, such as some carcinomas, most tumors. Heterogeneous refers to mixed populations of cells,
extracellular matrix may be observed in cytologic specimens. which are commonly found in aspirates of inflammatory lesions;
Collagen and osteoid consist of collections of smooth or fibril- however, some neoplasms will contain heterogeneous populations
lar magenta material, whereas chondroid matrix typically forms of cells (e.g., MCTs accompanied by eosinophils and fibroblasts
larger lakes of bright pink-to-purple material. Mucinous material [see Fig. 7.5] and squamous cell carcinomas with associated neu-
may be secreted by a variety of tumors, including salivary, bili- trophilic inflammation [see later]). The terms monomorphic and
ary, and intestinal carcinomas and myxomatous sarcomas. Mucin pleomorphic describe the morphologic appearance of cells within a
or myxoid matrix is pale blue to pink, and cells surrounded by single population. Monomorphic describes cells of a single lineage
mucin are often aligned in rows. Ultrasound gel may be a con- in which the cells have a uniform morphologic appearance (see
taminant on slides prepared from ultrasound-guided aspirates Fig. 7.4A). Monomorphic features typically are associated with
if the needle is not cleaned before expelling cells onto the slide. benign tumors, but a number of malignant tumors are cytologi-
Ultrasound gel appears as bright magenta, granular material when cally monomorphic. In contrast, pleomorphic is used to describe
stained with cytologic stains and, if abundant, may impair cyto- cells of a single lineage that have variable morphologic features
logic examination. (see Fig. 7.4B). Pleomorphic features comprise a set of criteria
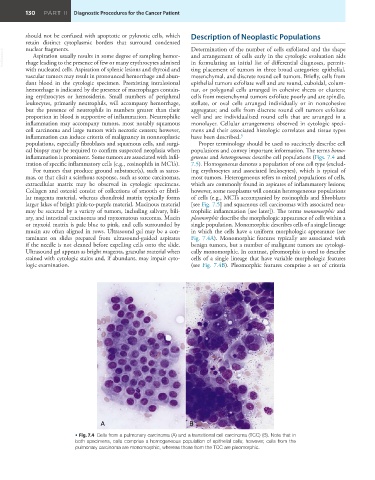
A B
• Fig. 7.4 Cells from a pulmonary carcinoma (A) and a transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) (B). Note that in
both specimens, cells comprise a homogeneous population of epithelial cells; however, cells from the
pulmonary carcinoma are monomorphic, whereas those from the TCC are pleomorphic.