Page 1104 - Veterinary Immunology, 10th Edition
P. 1104
VetBooks.ir
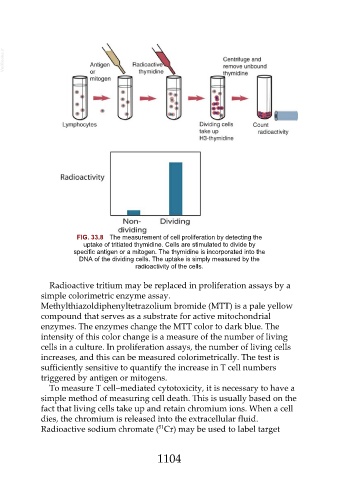
FIG. 33.8 The measurement of cell proliferation by detecting the
uptake of tritiated thymidine. Cells are stimulated to divide by
specific antigen or a mitogen. The thymidine is incorporated into the
DNA of the dividing cells. The uptake is simply measured by the
radioactivity of the cells.
Radioactive tritium may be replaced in proliferation assays by a
simple colorimetric enzyme assay.
Methylthiazoldiphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) is a pale yellow
compound that serves as a substrate for active mitochondrial
enzymes. The enzymes change the MTT color to dark blue. The
intensity of this color change is a measure of the number of living
cells in a culture. In proliferation assays, the number of living cells
increases, and this can be measured colorimetrically. The test is
sufficiently sensitive to quantify the increase in T cell numbers
triggered by antigen or mitogens.
To measure T cell–mediated cytotoxicity, it is necessary to have a
simple method of measuring cell death. This is usually based on the
fact that living cells take up and retain chromium ions. When a cell
dies, the chromium is released into the extracellular fluid.
51
Radioactive sodium chromate ( Cr) may be used to label target
1104