Page 118 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 118
100 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
Table 4.1 Distinguishing structural features of smooth, skeletal and cardiac muscle.
VetBooks.ir Cell shape Smooth muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle
Branched
Polygonal
Spindle-shaped
Length of 20–500 μm, Few mm to 10 cm 50–100 μm
individual cell up to 800 μm in the gravid
uterus
Diameter of 3–10 μm 10–100 μm 10–30 μm
individual cell
Nucleus number Single nucleus, central Many nuclei (up to several Single nucleus,
and location location, hundred, depending on central location,
elongate, fusiform length of cell; syncytium), spherical, ovoid
peripherally located,
flattened
Fibres Complex arrangement of Cross-banding Cross-banding
myofilaments, no cross-
banding
Special features Spheroid caveolae (with Narrow T tubules at the Expanded T tubules at the
2+
Ca pumps; association level of the A–I band level of the Z line,
with sarcoplasmic junction, triads diads
reticulum), no T system
Innervation Autonomic Somatic Autonomous stimulus
initiation and conduction,
autonomic innervation
Neuromuscular Nerve fibres passing Neuromuscular junction Gap junctions
relationship close to muscle cells, gap (motor end plate)
junctions
Occurrence Walls of many organs Locomotor apparatus Myocardium
Regenerative Limited Via satellite cells Conditional
capacity
Special features Dense bodies (areae Satellite cells (capable of Intercalated discs (disci
densae) forming new muscle cells) intercalares), gap junctions,
desmosomes, electrical
coupling
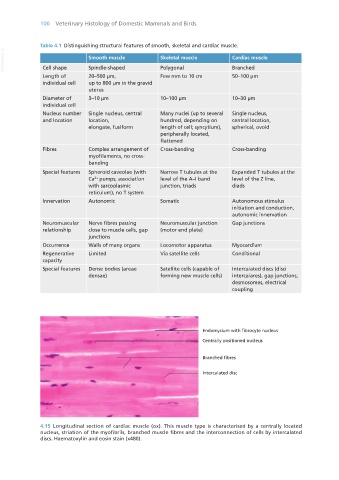
4.15 Longitudinal section of cardiac muscle (ox). This muscle type is characterised by a centrally located
nucleus, striation of the myofibrils, branched muscle fibres and the interconnection of cells by intercalated
discs. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x480).
Vet Histology.indb 100 16/07/2019 14:56