Page 139 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 139
Circulatory system (systema cardiovasculare et Iymphovasculare) 121
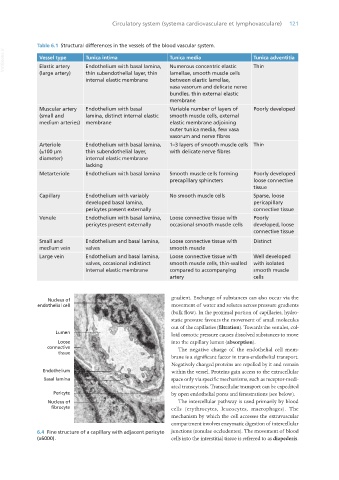
Table 6.1 Structural differences in the vessels of the blood vascular system.
VetBooks.ir Vessel type Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica adventitia
Endothelium with basal lamina,
Thin
Numerous concentric elastic
Elastic artery
(large artery) thin subendothelial layer, thin lamellae, smooth muscle cells
internal elastic membrane between elastic lamellae,
vasa vasorum and delicate nerve
bundles, thin external elastic
membrane
Muscular artery Endothelium with basal Variable number of layers of Poorly developed
(small and lamina, distinct internal elastic smooth muscle cells, external
medium arteries) membrane elastic membrane adjoining
outer tunica media, few vasa
vasorum and nerve fibres
Arteriole Endothelium with basal lamina, 1–3 layers of smooth muscle cells Thin
(≤100 μm thin subendothelial layer, with delicate nerve fibres
diameter) internal elastic membrane
lacking
Metarteriole Endothelium with basal lamina Smooth muscle cells forming Poorly developed
precapillary sphincters loose connective
tissue
Capillary Endothelium with variably No smooth muscle cells Sparse, loose
developed basal lamina, pericapillary
pericytes present externally connective tissue
Venule Endothelium with basal lamina, Loose connective tissue with Poorly
pericytes present externally occasional smooth muscle cells developed, loose
connective tissue
Small and Endothelium and basal lamina, Loose connective tissue with Distinct
medium vein valves smooth muscle
Large vein Endothelium and basal lamina, Loose connective tissue with Well developed
valves, occasional indistinct smooth muscle cells, thin-walled with isolated
internal elastic membrane compared to accompanying smooth muscle
artery cells
gradient. Exchange of substances can also occur via the
movement of water and solutes across pressure gradients
(bulk flow). In the proximal portion of capillaries, hydro-
static pressure favours the movement of small molecules
out of the capillaries (filtration). Towards the venules, col-
loid osmotic pressure causes dissolved substances to move
into the capillary lumen (absorption).
The negative charge of the endothelial cell mem-
brane is a significant factor in trans-endothelial transport.
Negatively charged proteins are repelled by it and remain
within the vessel. Proteins gain access to the extracellular
space only via specific mechanisms, such as receptor-medi-
ated transcytosis. Transcellular transport can be expedited
by open endothelial pores and fenestrations (see below).
The intercellular pathway is used primarily by blood
cells (erythrocytes, leucocytes, macrophages). The
mechanism by which the cell accesses the extravascular
compartment involves enzymatic digestion of intercellular
6.4 Fine structure of a capillary with adjacent pericyte junctions (zonulae occludentes). The movement of blood
(x6000). cells into the interstitial tissue is referred to as diapedesis.
Vet Histology.indb 121 16/07/2019 14:58