Page 144 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 144
126 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
distinguished in histological sections by its undulating
· elastic arteries (arteria elastotypica) and
VetBooks.ir · muscular arteries (arteria myotypica). appearance (artefactual contraction). The endothelium
is connected by endothelial cell processes to the smooth
ELASTIC ARTERIES (ARTERIA ELASTOTYPICA) muscle cells of the tunica media, which may also contrib-
ute to re-epithelialisation of the vessel wall.
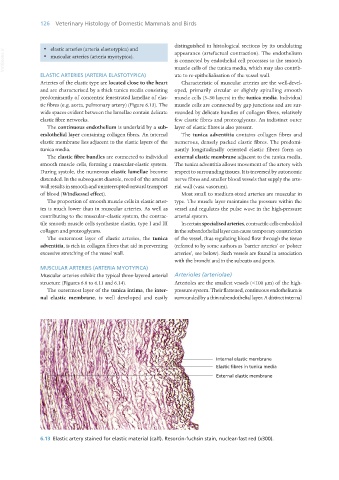
Arteries of the elastic type are located close to the heart Characteristic of muscular arteries are the well-devel-
and are characterised by a thick tunica media consisting oped, primarily circular or slightly spiralling smooth
predominantly of concentric fenestrated lamellae of elas- muscle cells (3–30 layers) in the tunica media. Individual
tic fibres (e.g. aorta, pulmonary artery) (Figure 6.13). The muscle cells are connected by gap junctions and are sur-
wide spaces evident between the lamellae contain delicate rounded by delicate bundles of collagen fibres, relatively
elastic fibre networks. few elastic fibres and proteoglycans. An indistinct outer
The continuous endothelium is underlaid by a sub- layer of elastic fibres is also present.
endothelial layer containing collagen fibres. An internal The tunica adventitia contains collagen fibres and
elastic membrane lies adjacent to the elastic layers of the numerous, densely packed elastic fibres. The predomi-
tunica media. nantly longitudinally oriented elastic fibres form an
The elastic fibre bundles are connected to individual external elastic membrane adjacent to the tunica media.
smooth muscle cells, forming a muscular-elastic system. The tunica adventitia allows movement of the artery with
During systole, the numerous elastic lamellae become respect to surrounding tissues. It is traversed by autonomic
distended. In the subsequent diastole, recoil of the arterial nerve fibres and smaller blood vessels that supply the arte-
wall results in smooth and uninterrupted onward transport rial wall (vasa vasorum).
of blood (Windkessel effect). Most small to medium-sized arteries are muscular in
The proportion of smooth muscle cells in elastic arter- type. The muscle layer maintains the pressure within the
ies is much lower than in muscular arteries. As well as vessel and regulates the pulse wave in the high-pressure
contributing to the muscular–elastic system, the contrac- arterial system.
tile smooth muscle cells synthesise elastin, type I and III In certain specialised arteries, contractile cells embedded
collagen and proteoglycans. in the subendothelial layer can cause temporary constriction
The outermost layer of elastic arteries, the tunica of the vessel, thus regulating blood flow through the tissue
adventitia, is rich in collagen fibres that aid in preventing (referred to by some authors as ‘barrier arteries’ or ‘polster
excessive stretching of the vessel wall. arteries’, see below). Such vessels are found in association
with the bronchi and in the subcutis and penis.
MUSCULAR ARTERIES (ARTERIA MYOTYPICA)
Muscular arteries exhibit the typical three-layered arterial Arterioles (arteriolae)
structure (Figures 6.8 to 6.11 and 6.14). Arterioles are the smallest vessels (<100 μm) of the high-
The outermost layer of the tunica intima, the inter- pressure system. Their flattened, continuous endothelium is
nal elastic membrane, is well developed and easily surrounded by a thin subendothelial layer. A distinct internal
6.13 Elastic artery stained for elastic material (calf). Resorcin-fuchsin stain, nuclear-fast red (x300).
Vet Histology.indb 126 16/07/2019 14:58