Page 191 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 191
Endocrine system (systema endocrinum) 173
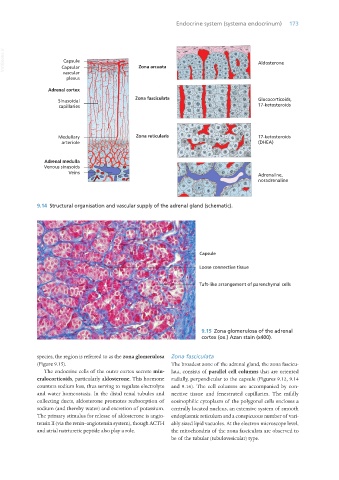
VetBooks.ir Capsule Zona arcuata Aldosterone
Capsular
vascular
plexus
Adrenal cortex
Zona fasciculata Glucocorticoids,
Sinusoidal
capillaries 17-ketosteroids
Medullary Zona reticularis 17-ketosteroids
arteriole (DHEA)
Adrenal medulla
Venous sinusoids
Veins
Adrenaline,
noradrenaline
9.14 Structural organisation and vascular supply of the adrenal gland (schematic).
9.15 Zona glomerulosa of the adrenal
cortex (ox.) Azan stain (x400).
species, the region is referred to as the zona glomerulosa Zona fasciculata
(Figure 9.15). The broadest zone of the adrenal gland, the zona fascicu-
The endocrine cells of the outer cortex secrete min- lata, consists of parallel cell columns that are oriented
eralocorticoids, particularly aldosterone. This hormone radially, perpendicular to the capsule (Figures 9.12, 9.14
counters sodium loss, thus serving to regulate electrolyte and 9.16). The cell columns are accompanied by con-
and water homeostasis. In the distal renal tubules and nective tissue and fenestrated capillaries. The mildly
collecting ducts, aldosterone promotes reabsorption of eosinophilic cytoplasm of the polygonal cells encloses a
sodium (and thereby water) and excretion of potassium. centrally located nucleus, an extensive system of smooth
The primary stimulus for release of aldosterone is angio- endoplasmic reticulum and a conspicuous number of vari-
tensin II (via the renin–angiotensin system), though ACTH ably sized lipid vacuoles. At the electron microscope level,
and atrial natriuretic peptide also play a role. the mitochondria of the zona fasciculata are observed to
be of the tubular (tubulovesicular) type.
Vet Histology.indb 173 16/07/2019 15:00