Page 194 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 194
176 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
Autonomic nerve
VetBooks.ir Capillary with
fibre with synapse
Support cell
(Type II cell) erythrocyte
Principal cell
(Type I cell)
Principal cell
(Type I cell)
Support cell
(Type II cell)
Support cell
Autonomic nerve fibre (Type II cell)
with synapse
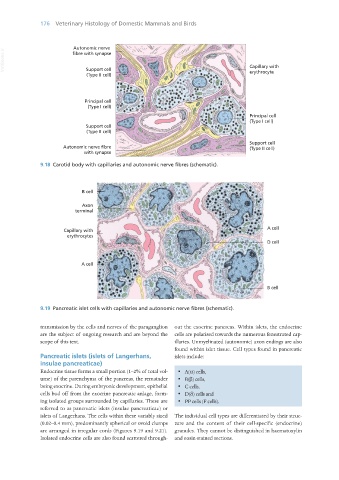
9.18 Carotid body with capillaries and autonomic nerve fibres (schematic).
9.19 Pancreatic islet cells with capillaries and autonomic nerve fibres (schematic).
transmission by the cells and nerves of the paraganglion out the exocrine pancreas. Within islets, the endocrine
are the subject of ongoing research and are beyond the cells are polarised towards the numerous fenestrated cap-
scope of this text. illaries. Unmyelinated (autonomic) axon endings are also
found within islet tissue. Cell types found in pancreatic
Pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans, islets include:
insulae pancreaticae)
Endocrine tissue forms a small portion (1–2% of total vol- · A(α) cells,
ume) of the parenchyma of the pancreas, the remainder · B(β) cells,
being exocrine. During embryonic development, epithelial · C cells,
cells bud off from the exocrine pancreatic anlage, form- · D(δ) cells and
ing isolated groups surrounded by capillaries. These are · PP cells (F cells).
referred to as pancreatic islets (insulae pancreaticae) or
islets of Langerhans. The cells within these variably sized The individual cell types are differentiated by their struc-
(0.02–0.4 mm), predominantly spherical or ovoid clumps ture and the content of their cell-specific (endocrine)
are arranged in irregular cords (Figures 9.19 and 9.21). granules. They cannot be distinguished in haematoxylin
Isolated endocrine cells are also found scattered through- and eosin-stained sections.
Vet Histology.indb 176 16/07/2019 15:00