Page 192 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 192
174 Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds
VetBooks.ir
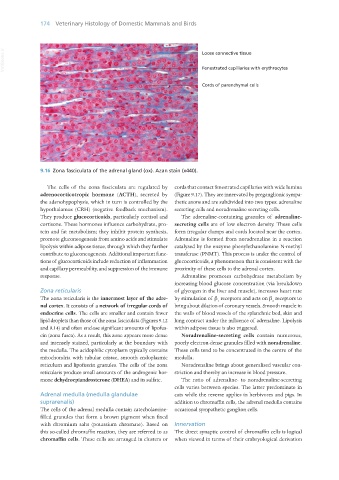
9.16 Zona fasciculata of the adrenal gland (ox). Azan stain (x440).
The cells of the zona fasciculata are regulated by cords that contact fenestrated capillaries with wide lumina
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), secreted by (Figure 9.17). They are innervated by preganglionic sympa-
the adenohypophysis, which in turn is controlled by the thetic axons and are subdivided into two types: adrenaline
hypothalamus (CRH) (negative feedback mechanism). secreting cells and noradrenaline secreting cells.
They produce glucocorticoids, particularly cortisol and The adrenaline-containing granules of adrenaline-
cortisone. These hormones influence carbohydrate, pro- secreting cells are of low electron density. These cells
tein and fat metabolism; they inhibit protein synthesis, form irregular clumps and cords located near the cortex.
promote gluconeogenesis from amino acids and stimulate Adrenaline is formed from noradrenaline in a reaction
lipolysis within adipose tissue, through which they further catalysed by the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyl
contribute to gluconeogenesis. Additional important func- transferase (PNMT). This process is under the control of
tions of glucocorticoids include reduction of inflammation glucocorticoids, a phenomenon that is consistent with the
and capillary permeability, and suppression of the immune proximity of these cells to the adrenal cortex.
response. Adrenaline promotes carbohydrate metabolism by
increasing blood glucose concentration (via breakdown
Zona reticularis of glycogen in the liver and muscle), increases heart rate
The zona reticularis is the innermost layer of the adre- by stimulation of β receptors and acts on β receptors to
1 2
nal cortex. It consists of a network of irregular cords of bring about dilation of coronary vessels. Smooth muscle in
endocrine cells. The cells are smaller and contain fewer the walls of blood vessels of the splanchnic bed, skin and
lipid droplets than those of the zona fasciculata (Figures 9.12 lung contract under the influence of adrenaline. Lipolysis
and 9.14) and often enclose significant amounts of lipofus- within adipose tissue is also triggered.
cin (zona fusca). As a result, this zone appears more dense Noradrenaline-secreting cells contain numerous,
and intensely stained, particularly at the boundary with poorly electron-dense granules filled with noradrenaline.
the medulla. The acidophilic cytoplasm typically contains These cells tend to be concentrated in the centre of the
mitochondria with tubular cristae, smooth endoplasmic medulla.
reticulum and lipofuscin granules. The cells of the zona Noradrenaline brings about generalised vascular con-
reticularis produce small amounts of the androgenic hor- striction and thereby an increase in blood pressure.
mone dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and its sulfate. The ratio of adrenaline- to noradrenaline-secreting
cells varies between species. The latter predominate in
Adrenal medulla (medulla glandulae cats while the reverse applies in herbivores and pigs. In
suprarenalis) addition to chromaffin cells, the adrenal medulla contains
The cells of the adrenal medulla contain catecholamine- occasional sympathetic ganglion cells.
filled granules that form a brown pigment when fixed
with chromium salts (potassium chromate). Based on Innervation
this so-called chromaffin reaction, they are referred to as The direct synaptic control of chromaffin cells is logical
chromaffin cells. These cells are arranged in clusters or when viewed in terms of their embryological derivation
Vet Histology.indb 174 16/07/2019 15:00