Page 199 - Veterinary Histology of Domestic Mammals and Birds, 5th Edition
P. 199
Digestive system (apparatus digestorius) 181
VetBooks.ir
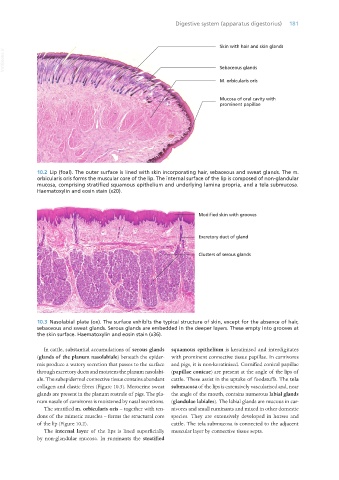
10.2 Lip (foal). The outer surface is lined with skin incorporating hair, sebaceous and sweat glands. The m.
orbicularis oris forms the muscular core of the lip. The internal surface of the lip is composed of non-glandular
mucosa, comprising stratified squamous epithelium and underlying lamina propria, and a tela submucosa.
Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x20).
10.3 Nasolabial plate (ox). The surface exhibits the typical structure of skin, except for the absence of hair,
sebaceous and sweat glands. Serous glands are embedded in the deeper layers. These empty into grooves at
the skin surface. Haematoxylin and eosin stain (x36).
In cattle, substantial accumulations of serous glands squamous epithelium is keratinised and interdigitates
(glands of the planum nasolabiale) beneath the epider- with prominent connective tissue papillae. In carnivores
mis produce a watery secretion that passes to the surface and pigs, it is non-keratinised. Cornified conical papillae
through excretory ducts and moistens the planum nasolabi- (papillae conicae) are present at the angle of the lips of
ale. The subepidermal connective tissue contains abundant cattle. These assist in the uptake of foodstuffs. The tela
collagen and elastic fibres (Figure 10.3). Merocrine sweat submucosa of the lips is extensively vascularised and, near
glands are present in the planum rostrale of pigs. The pla- the angle of the mouth, contains numerous labial glands
num nasale of carnivores is moistened by nasal secretions. (glandulae labiales). The labial glands are mucous in car-
The stratified m. orbicularis oris – together with ten- nivores and small ruminants and mixed in other domestic
dons of the mimetic muscles – forms the structural core species. They are extensively developed in horses and
of the lip (Figure 10.2). cattle. The tela submucosa is connected to the adjacent
The internal layer of the lips is lined superficially muscular layer by connective tissue septa.
by non-glandular mucosa. In ruminants the stratified
Vet Histology.indb 181 16/07/2019 15:00